* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
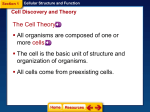
Biology Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function Section 1 I. Objectives for section 7-1: Cell Discovery and Theory A. Relate microscope technology to discovers of the cell B. Compare and contrast light and electron microscopes C. State the principles of the cell theory D. Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Section 1 II. Five scientists responsible Cell Theory A. Microscope invented in 1600’s B. In 1665, English scientist, Robert Hooke was the first to see and name cells for Section 1 1. Saw little boxes in slice of cork that reminded him of small rooms in which monks lived Section 1 C. In 1675, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Dutch scientist, discovered single celled organisms Section 1 1. Leeuwenhoek’s microscope discovers Spirogyra, a single- celled organism Section 1 D. 1838 - Matthias Schleiden (German) – stated all PLANTS and plant parts are composed of cells Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells Section 1 E. 1839 - Theodor Schwann (German) stated all ANIMALS and animal organs are composed of cells Nerve cells in your brain Section 1 F. 1858 - Rudolph Virchow (German) – stated all cells come only from existing cells (NOT spontaneous generation) First to see leukemia cells (in purple) Section 1 Cellular Structure and Function G. The Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are basic unit of structure and organization of organisms 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Section 1 Cellular Structure and Function III. Cell Discovery and Theory A. Light microscopes utilize series of glass lenses and visible light to magnify images 1. Magnifies living or nonliving things up to 2,000 times actual size Mite Section 1 Cellular Structure and Function B. Electron microscopes utilize magnets to aim a beam of electrons at a cell to produce an image 1. Magnifies images up to 500,000 times actual size 2. Spider leg --inspiration for making post-it notes Section 1 3. Transmission electron microcsope (TEM) electrons pass through a specimen a. Can reveal a cell’s internal structure b. Only use dead specimens Virus Image Section 1 4. Scanning EMelectrons bounce off a specimen (coated in metal), forming a 3D image of specimen a. Only nonliving samples can be used Fly Head and Leg Section 1 5. Scanning Tunneling (STM) Microscopes a. Charged tip of probe allows electrons to “tunnel” through small gaps in specimens b. Computer generated 3-D images created c. Living objects (DNA) and atoms can be viewed Silicon Atom Section 1 Two basic cell types What differences do you see? Section 1 Cellular Structure and Function IV. Two Basic Cell Types A. Prokaryotic Cell evolved about 3.5 billion years ago 1. Simple structure 2. Contains a plasma membrane 3. Does not contain membranebound organelles 4. Example: bacteria Section 1 Cellular Structure and Function B. Eukaryotic Cells have a more complex structure 1. Contains plasma membrane 2. Contains membranebound organelles Section 2 I. Objectives for section 7-2: The Plasma Membrane A. State the function of the cell membrane B. Explain how proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol play a role in the plasma membrane Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function II. Plasma Membrane is a thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its environment A. Allows nutrients into and wastes to leave the cell Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function B. Selective Permeability: controls movement of substances into and out of cell C. Controls amount of substances entering and leaving the cell Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function D. Composed of phospholipid bilayer 1. Composed of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group 2. Polar (partially charged) head and 2 nonpolar (no charge) tails Section 2 Phospholipid bilayer Lipid bilayer E. Overall picture Phospholipid molecule Lipid bilayer makes up the cell membrane Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function F. Fluid Mosaic Model 1. Bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in membrane Transport protein Section 2 2. Nonpolar tails on inside do not allow water-soluble substances to pass through easily a. Allows cell to separate inside environment from the outside b. Proteins are held in membrane in a similar fashion Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function III. Other components of plasma membrane A. Proteins act as a support structure Section 2 1. Receptor proteins transmit signals inside the cell a. “intercellular communication” Section 2 2. Transport proteins: aid movement of substances into and out of cells Section 2 3. Marker proteins: attached to a carbohydrate on cell’s surface and advertise cell type a. Will recognize foreign invaders including transplanted organs!! Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function B. Cholesterol prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together Section 2 Cellular Structure and Function C. Carbohydrates identify chemical signals Section 3 I. Objectives for section 7-3: Structures and organelles A. Identify an eukaryote’s organelles and their functions B. State differences between plant and animal cells Section 3 II. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow specialization and separation of function within the cell Section 3 Cellular Structure and Function A. Plant and Animal Cell Structures Animal Cell Plant Cell Section 3 Cellular Structure and Function Animal Cell Organelles Section 3 Cellular Structure and Function Plant Cell Organelles Section 3 III. You will be divided into groups to present the organelles A. Must present organelle’s function B. Must state which type of cell it can be found in C. Must be able to respond to and answer questions about organelles D. Must present two labeled graphics of your organelles on a poster Section 3 E. Categories include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cytoplasm and cytoskeleton Nucleus, nuclear pore, and nucleolus Ribosomes, centrioles, and chromatin (DNA) Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus and vesicles Vacuole and lysosomes Mitochondria and chloroplasts Cell Wall, cilia and flagella