* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Role of Spirometry and Exhaled Nitric Oxide To Predict
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
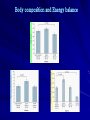
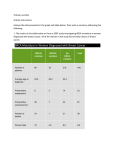
Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Congenital Deficiency of the Leptin Receptor I. Sadaf Farooqi, M.B., B.S., Ph.D., Teresia Wangensteen, M.D., Stephan Collins, Ph.D., Wendy Kimber, Ph.D., Giuseppe Matarese, M.D., Ph.D., et al. N Engl J Med Jan.18, 2007;356;3 R2. Hwang Seung-Joon Background (1) ◆Severe early-onset obesity -Classically, assess the neurologic, endocrinologic, genetic condition -Several monogenic disorders : Obesity itself is the predominant presenting feature Disruption of the hypothalamic leptin – melanocortin signaling pathway Background (2) -12 subjects with congenital leptin deficiency due to loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding leptin have been identified -Only 1 mutation in the leptin-receptor gene (LEPR) has been reported, in 3 severely obese adult siblings from a consanguineous family of Algerian origin -Studied 300 subjects with severe, early-onset obesity Methods (1) ●Subjects “Genetics of Obesity Study (GOOS) cohort” : 2100 unrelated probands with severe obesity of early onset (before 10 years of age) 300 were selected to determine the prevalence of leptin receptor mutations -Mean BMI standard-deviation score for the group screened : 4.5±1.2 -SIM1, NHLH2, CPE, MCHR1, MCHR2 : No mutations Methods (2) ●Detection of Mutations and Genotyping -Genomic DNA was isolated from leukocytes derived from whole blood -Coding region of the LEPR gene was amplified with the use of the PCR and was then sequenced -Also sequenced LEPR gene in impartially selected nonobese control subjects -100 alleles from each of 3 population-derived cohorts : White European origin, South Asian origin, Turkish origin Methods (3) ●Body Composition, Growth, and Energy Balance -Body composition : Anthropometric methods & Whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry -Resting metabolic rate : Indirect calorimetry after 12hr-overnight fasting ●Metabolic & Endocrine status -Fasting blood samples leptin, glucose, insulin, thyrotropin, free thyroxine, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), folliclestimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, estradiol, testosterone Methods (4) ●Lymphocyte count & Function -Lymphocytes Isolation -Cell phenotypes : Measured by cytofluorometric analysis -Lymphocyte counts & Proliferative responses in subjects with leptin-receptor deficiency (Vs. 46 control subjects matched for age) ●Statistical Analysis -Expression : Means ± SD -unpaired Student’s t-test -P value : two-sided tests (Statistical significance : p <0.05) Results Detection of Mutations and Family Studies Pedigrees of Consanguineous Families with Mutations in the Leptin-Receptor Gene (1) Pedigrees of Consanguineous Families with Mutations in the Leptin-Receptor Gene (2) Pedigrees of Nonconsanguineous Families with Mutations in the Leptin-Receptor Gene Mutations in the Leptin-Receptor Gene Functional Analysis of Mutant Receptors A409E, W664R, H684P : Complete loss of signaling R612H : Some residual ability to phosphorylate STAT3 in response to leptin Clinical phenotype for Leptin receptor deficiency -LEPR mutation group (10) VS -Congenital leptin deficiency group (5) VS -MC4R (Melanocortin 4 receptor) mutation group (5) Body composition & Energy balance Metabolic & Endocrine function Immune function Body composition and Energy balance Metabolic and Endocrine function Immune function ●Leptin-receptor deficient subject : Marked reduction in the CD4+ T-cell count & Reduced T-cell proliferation -Leptin-receptor–deficient subjects (mean, 988±186 cells / mm3 ; 42±13%) -Control subjects (mean, 1100±892 cells / mm3 ; 44±7%) Conclusions ●LEPR mutation : Hyperphagia, Severe obesity, Alterations in immune function, Delayed puberty due to hypogonadotropic-hypogonadism : Should be considered in the differential diagnosis in any child with hyperphagia and severe obesity in the absence of developmental delay or dysmorphism