* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of Cell Structure
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
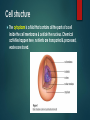
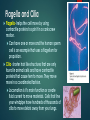
Overview of Cell Structure CELLS ARE THE BASIC CELLS ARE THE BASIC STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL OF ALL LIVING THINGS. ALL CELLS VERY IN SHAPE AND FUNCTION, BUT ALL PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS HAVE MANY COMMON FEATURES. The Cell Theory States All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the smallest entity that retains the property of life. New cells arise only from cells that already exist. Classification of cells • Eukaryotic- A type of cell that has a true nucleus. The nuclear membrane surrounds a well-defined nucleus. • Prokaryotic- A type of cell that does not have a nuclear membrane and no true nucleus. Cell structure The cytoplasm is a fluid that contains all the parts of a cell inside the cell membrane & outside the nucleus. Chemical activities happen here, nutrients are transported & processed, wastes are stored. Cell Membrane Outermost boundary of the cell where many of the cells activities take place. Made of proteins and a bilayer(double) of lipid (fat)molecules Holds the cell content in place Regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains threadlike chromosomes made of genes Chromosomes are made of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which is the genetic material of life Pores in the envelope allow some things to pass through and not others. Nucleolus A small, spherical structure located inside the nucleus. It is associated with RNA. It is involved in making genetic material called rRNA and directs the formation of ribosomes. Flagella and Cilia Flagella- helps the cell move by using contractile proteins to spin it in a corkscrew motion. Can have one or more and the human sperm cell is an example that uses a flagellum for propulsion. Cilia- shorter hair like structures that are only found in animal cells and have contractile proteins that cause tem to move. They move more in a coordinated fashion. Locomotion is it’s main function or create fluid current to move materials. Cells that line your windpipe have hundreds of thousands of cilia to move debris away from your lungs. Cytoplasmic Organelles YOU WILL EACH PICK A CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLE TO RESEARCH. • YOU MUST CREATE A POWERPOINT SLIDE ABOUT YOUR ORGANELLE • THE SLIDE MUST BE IN BULLET FORMAT AND CONTAIN THE FOLLOWING… • A detailed description of It’s role in the cell • Which cells they can be found in • It’s shape • A picture/diagram • You will present your findings to the class Cytoplasmic Organelles MITOCHONDRIA RIBOSOMES ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM GOLGI APPARATUS LYSOSOMES MICROFILAMENTS AND MICROTUBULES CHLOROPLASTS VACUOLE Answer the Following Questions Outline the major concepts of the cell theory. What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? Describe the function of the nucleus. What are chromosomes and genes? Describe the function of the cell membrane. Describe the structure and function of centrioles. Why would muscle tissue cells require more mitochondria than fat cells? What roles does the Golgi apparatus play in the transport of materials into and out of the cell? What kinds of materials does it package? What role does lysosomes play in in the human body’s defence mechanism? Explain. Which organelle is involved with cellular respiration and explain? Describe using a Venn Diagram similarities and differences between plant and animal cells.