* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANSWER - EdWeb
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
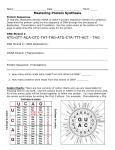
1st Semester Final Exam Study Guide Answers to Questions #56-106 (Genetics & DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis) 1) Play the slide show 2) Read the question, answer on your own and then click to show the correct answer 3) Click to go to the next question GENETICS (CHAPTERS 11, 12-4 & 14) 56. What is heredity? ANSWER: Heredity is the passing of traits from parent to offspring 57. What do you call the genetic makeup of an organism? ANSWER: Genotype 58. What is the outward appearance of a trait called? ANSWER: Phenotype 59. What do the terms homozygous and heterozygous mean? Give an example of each genotype. ANSWER: Homozygous means the alleles are the same (Ex: HH, gg) Heterozygous means the alleles are different (Ex: Hh, Gg) 60. Who is known as the “Father of Genetics?” ANSWER: Gregor Mendel 61. What term describes when two alleles affect the phenotype of an organism by blending together? ANSWER: Incomplete Dominance Ex: Red flowers crossed with white flowers make pink flowers. 62. What term describes two alleles affecting the phenotype of an organism but without blending? ANSWER: Codominance Ex: Red flowers crossed with white flowers make red & white flowers. 63. What is a trait determined by more than one pair of alleles or more than one gene? (Know examples) ANSWER: Polygenic Traits Examples are hair color, eye color, skin color & height – they are all controlled by multiple genes. 64. What do you call traits determined by three or more alleles? (Know examples) ANSWER: Multiple allelic traits An example is human blood types – the three alleles are A, B and O. 65. What genotypes (letters) are used to represent males and females? ANSWER: Males = XY Females = XX 66. Who is more likely to inherit a sex-linked condition – men or women? EXPLAIN WHY. ANSWER: Males – they have only one X chromosome so they only need to inherit one copy of the gene rather than two copies. 67. If chromosomes do not separate correctly during the process of meiosis, this is called ____. ANSWER: Nondisjunction 68. If chromosomes do not separate correctly during meiosis, how does this change the number of chromosomes in the gametes that form? ANSWER: The gametes either have extra or missing chromosomes 69. Describe the following chromosomal mutations: a. Inversion b. Translocation ANSWER: a. Inversion is when part of a chromosome is reversed or switched around in the wrong order b. Translocation is two chromosomes exchange information when they are not supposed to Know your chromosome mutations! 70. What is a carrier – what genotype is used to describe a carrier? ANSWER: Carriers are individuals who have one copy of a recessive allele. They are heterozygous 71. If a trait is sex-linked, who can never be a carrier for it? ANSWER: MALES 72. What do you call a diagram that allows you to follow or trace a trait through several generations? ANSWER: Pedigree 73. For a pedigree, what do circles and squares represent? ANSWER: Circles = Females Square = Males 74. For a pedigree, if circles or squares are half-shaded, these individuals are ____. ANSWER: Carriers 75. What do you call a picture of your chromosomes that arrange them into pairs and then orders them by size? Why are these pictures important? ANSWER: - Karyotypes! - They are important because it can help detect genetic disorders 76. Based on the descriptions below, identify the correct genetic disorder. ANSWER: a. Individual may have both female and male characteristics because their sex chromosomes are XXY = KLINEFELTER’S SYNDROME b. Individuals have mental retardation, muscle weakness and short stature because they have three chromosomes at position twenty-one = DOWN SYNDROME 76. Based on the descriptions below, identify the correct genetic disorder. ANSWER: c. Individuals have deterioration of brain tissue in the middle ages because of a dominant gene = HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE d. Females may have developmental or reproductive issues because they have only one X chromosome = TURNER’S SYNDROME 76. Based on the descriptions below, identify the correct genetic disorder. ANSWER: e. Individuals cannot clot their blood because they have a recessive sex-linked gene= HEMOPHILIA 77. Name three methods for genetic screening. ANSWER: a) Blood tests (check for presence of proteins) b) Amniocentesis = extract fluid surrounding baby and test c) Chronic Villi Sampling = extract tissue from placenta and test 78. What is the identification and manipulation/transfer of genes from one organism to a different organism called? ANSWER: GENETIC ENGINEERING 79. Name four practical uses of genetic engineering/DNA technology. ANSWER: a) Medicine/vaccines b) Useful bacteria c) Food crops (more vitamins/nutrients, help in growth) d) Alter plants (resistant to pesticides/insects, no fertilizer) DNA, RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (SECTIONS 12-1 TO 12-4) 80. What does DNA stand for? ANSWER: Deoxyribonucleic acid KNOW THE PARTS OF DNA!! 81. What does RNA stand for? ANSWER: Ribonucleic acid 82. Name the 3 parts of a nucleotide (the “building blocks” of DNA) ANSWER: a. Sugar b. Phosphate c. Nitrogen base 83. Name the 4 bases in DNA. How do they pair up? ANSWER: Adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine Adenine pairs to Thymine Cytosine pairs to Guanine 84. What is the difference between a purine and a pyrimidine? ANSWER: Purines = two chemical rings (adenine & guanine) Pyrimidines = one chemical ring (thymine & cytosine) 85. What type of chemical bond forms between sugars and phosphates? ANSWER: Covalent bond 86. What type of chemical bond forms between nitrogen bonds? ANSWER: Hydrogen bond 87. What is the shape of DNA? Who are the scientists who discovered it? ANSWER: DNA has a helix shape (a twisted ladder) Watson & Crick are the scientists who discovered it. 88. What is a mutation? Is it always harmful? ANSWER: Mutations are permanent changes in DNA. They can be harmful BUT can also be helpful or have no effect on the organism. 89. Describe the following gene mutations: a. Point mutation ANSWER: a. Point mutations mean one base is substituted for the wrong base (Ex: Adenine is accidentally put where Guanine should be) – it may or may not affect the organism. 89. Describe the following gene mutations: b. Frameshift mutation ANSWER: Frameshift mutations mean you add or delete one nucleotide – it moves all the other bases over one place & changes the entire protein that gets produced. 90. Why is DNA replication referred to as “semi-conservative?” ANSWER: Replication is called “semi-conservative” because whenever new DNA is made, one strand is old and one strand is new. 91. List all the differences between DNA and RNA. ANSWER: DNA a) Deoxyribose sugar RNA a) Ribose sugar b) ACGT bases T = thymine b) ACGU bases U = uracil c) double-stranded helix c) single-stranded & no helix 92. Name the function of each type of RNA: a. mRNA b. tRNA c. rRNA ANSWER: a. mRNA = copies the code or “message” of DNA & sends it out to the ribosome b. tRNA = carries the amino acid over to the ribosome (amino acids make up a protein) c. rRNA = makes up the structure of the ribosome 93. Name the process that will make RNA from DNA. ANSWER: Transcription 94. What is a codon? ANSWER: A codon represents three mRNA nucleotides that determines one amino acid (for the protein) 95. Using the codon chart, what amino acid is produced from each codon listed below? ANSWER: ACG = threonine (Thr) GUG = valine (Val) UGG = Tryptophan (Trp) 96. Using the codon chart, what codon is the START codon for all proteins? What amino acid does this codon code for? ANSWER: AUG is the start codon. Methionine (Met) is the amino acid. 97. Using the codon chart, what are the three STOP codons that tell the cell to stop making a protein? ANSWER: UAA UAG UGA 98. Name the process that makes proteins from RNA. ANSWER: Translation 99. What do proteins consist of? What types of bonds link these components together to make a protein? ANSWER: Proteins consist of AMINO ACIDS. Peptide bonds link amino acids together. 100. Write the complementary strand to the strand of DNA shown under the process of REPLICATION. A T T C C G T C A A A T A A G G CA G T T T *You’re making a matching strand of DNA! 101. Write the complementary strand to the strand of DNA shown under the process of TRANSCRIPTION. A T T C C G T C A A A UA A G GC A G UU U *You’re making a matching strand of RNA! 102. A given piece of DNA contains 20% adenine. How much thymine should be present A + T + C + G = 100% A = T; C = G (base pair rules) A=20% so… T=20% 103. A given piece of DNA contains 10% cytosine. How much adenine should be present? A + T + C + G = 100% A = T; C = G (base pair rules) C=10% so… G=10% C+G= 20% so… A+T=80% A=T so… A=40% 104. Label the following piece of DNA. Use a D for the sugar, P for the phosphates, and the letter A, C, G, T for the bases. Circle a nucleotide. 105. From the given strand of DNA, write the protein that would result. In order to get full credit on the test, be sure to include the mRNA strand, tRNA strand, group the codons, and circle and link the amino acids together. 1. Make mRNA by base pairing to DNA 2. Bracket every three bases on mRNA to show the codons 3. Write in the correct amino acid for each codon 4. Circle and link together amino acids starting with “Met” until you reach a “Stop.” The circled and linked amino acids represent your protein. 5. Fill in tRNA after writing amino acids by base pairing to mRNA 6. Bracket tRNA to amino acid to show anticodons