* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cognitive Disorders
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dementia with Lewy bodies wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
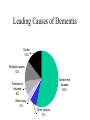
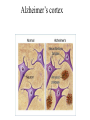
•Clear organic causes, where primary symptom is a significant deficit in cognitive ability •changes in the person’s personality and behavior (due to the brain disorder) Issues in Diagnosis of CDs • What is the cause of the pathology? – e.g., pseudodementia vs. progressive disease • Where is the location of the damage? • How are psychosocial factors involved? Prevalence 5 million Americans suffer from Alzheimer’s (24 million worldwide estimate*): 1 in 10 over 65 nearly half of those over 85 • 2.7 million have MCI (mild cognitive impairment) • 2 million+ Americans injure their heads annually *Very little is known about the prevalence of dementia outside the more developed countries (Europe, North America, Australasia and Japan), so it is difficult to estimate the number of cases of dementia worldwide Three major classes of CD • Delirium • Dementia • Amnestic Disorders Delirium • Acute onset • Confusion, disorientation • Caused by: – – – – – drug intoxication and/or withdrawal hyponatremia and/or malnutrition infections or other physical illnesses head injury surgery (e.g., heart) Symptoms of Dementia • Gradual onset • The Four A’s: – Amnesia (memory impairment) – Aphasia (language disturbance) – Apraxia (inability to carry out motor activities despite intact motor function) – Agnosia (failure to recognize or identify objects despite intact sensory functioning) • Disturbance in executive functioning Factors in onset of dementia • Degenerative processes (Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, etc.) • Repeated CVAs • Infectious diseases (e.g., HIV), tumors, neurotoxins Subtypes of dementia • Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type • Vascular Dementia • Subcortical dementias Leading Causes of Dementia Stroke 14% Multiple causes 12% Alzheimer's disease 55% Parkinson's disease 8% Brain injury 4% Other causes 7% Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type • Most common form of dementia • results not only in physical, but social, death • Video (Larry Gorrell, Ab Psy #10 or from Faces) Alzheimer’s • Beta-amyloid – Protein collects in clumps or plaques in the cortex in between neurons – damages or kills the neurons • Neurofibrillary tangles – Protein filaments IN the neurons get twisted; interferes with neural communication and eventually kills the neurons • Causes? – What causes the amyloid protein to form? – ApoE4 (three fold increase) Alzheimer’s cortex Alzheimer’s (prevention and treatment) • Treatment – Biological attempts to slow cognitive decline (have only a minor effect) – Psychosocial treatment • No strong data on prevention. Possibilities? – – – – – Antioxidant vitamins Folate Ginkgo biloba NSAIDs Crossword puzzles • Several current clinical trials for prevention Amnestic Disorders • Memory problems without other signs of dementia – Anterograde amnesia – Retrograde amnesia Amnestic Disorders • Causes – Psychogenic (already discussed) – Acquired brain injury • Head trauma • Drug use (e.g., Korsakoff’s syndrome -- video)