* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. Weber`s Science Classroom
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
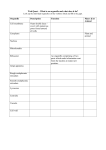
Chapter 3: Section 1 Note WorksheetCell Structure pages. 70-77 Cell: the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions Prokaryotic Cell: cells without membrane-bound structures. Only found in one-celled organisms such as bacteria. Eukaryotic Cell: cells with membrane-bound structures. Examples are protists, fungi, plant and animal cells. Cell Organization: each cell in your body has a specific function just like each part of the cell performs a specific function. Organelles: structure in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that can act as a storage site, process energy, move materials or manufacture substances. Tissues: a group of similar cells that work together to do one job. Each cell in a tissue does its part to keep the tissue alive. Organ: a structure made up of two or more different types of tissues that work together. Organ System: a group of organs working together to perform a certain function. In a many-celled organism, several systems work together in order to perform life functions efficiently. 1. What is the difference between the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum? The rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not. Organelle Classification Organelle Name Organelle Definition Energy Processing Mitochondria The “powerhouse” of the cell, releases energy from food. Energy Processing Chloroplasts Gives plant cells their green color (chlorophyll) and helps the plant make its food. Only found in plant cells. Recycling Lysosomes Break down food and wastes in the cell Manufacturing Ribosomes Makes proteins for the cell. Transport and Storage Golgi Bodies Small structures that sort proteins and other cellular substances and package them into membrane-bound structures called vesicles. These vesicles transport material from one part of the cell to another part of the cell. Transport and Storage Endoplasmic Reticulum The “hallways” of the cell where material is distributed throughout the cell. Rough means ribosomes attached and smooth means no ribosomes attached. Organelle Organelle Definition Nucleus Controls all the cell’s activities, houses the DNA of the cell. Nucleolus The inside part of the nucleus that contains the ribosome making material. Cytoskeleton The organelles inside the cell membrane that provide the cell shape. Cell Membrane A semi-permeable membrane that allows food and oxygen into the cell and lets wastes out of the cell. Vacuole Temporary storage facility for food, wastes and liquids. Cell Wall Composed of cellulose, grows, changes shape and protects the cell. Only found in plant cells. Organelles found in each type of cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell_________________________ 1. Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 1. Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 2. Nucleus 2. Nucleus 3. Nucleolus 3. Nucleolus 4. Mitochondria (Mitochondrion) ` 4. Mitochondria (Mitochondrion) 5. Lysosome 5. Lysosome 6. Golgi Bodies 6. Golgi Bodies 7. Cell Membrane 7. Cell Membrane 8. Central Vacuole 8. Vacuoles 9. Ribosome 9. Ribosome 10. Chloroplast 10. Cytoskeleton 11. Cell Wall