* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 - Tolland High School
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
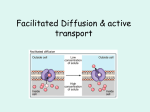
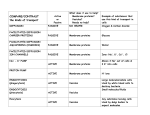
Chapter 4 Passive Transport & Active Transport Cell Membrane Review: • Selectively Permeable Membrane- the cell membrane only allows specific substances to pass through it Passive Transport • Passive transport moves substances from higher concentration to lower concentration • Passive transport does not require any energy (ATP) Concentration Gradient • A concentration gradient is a range in concentration across a space • Concentrations change from high low Equilibrium • Equilibrium is a condition when the concentration of a substance is equal in all areas Equilibrium Diffusion • Diffusion is the movement of molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration by random movement of the molecules Lower Concentration Higher Concentration Osmosis • Osmosis is the diffusion of water(H2O) through a selectively permeable membrane • Water moves to areas with less pure water and more dissolved solutes(like salt or sugar) Solutions(review) • Solute- the substance that gets dissolved – Ex: salt, sugar, kool-aid, chocolate milk mix • Solvent- the substance that dissolves another substance – Ex: water, alcohol, milk Types of Solutions • Hypertonic Solutions- water diffuses out of the cell – A higher concentration of solute outside of the cell draws water out of the cell – Cells will shrivel and shrink in a hypertonic solution Types of Solutions • Hypotonic Solutions- water diffuses into the cell – A lower concentration of solute outside the cell causes water to enter the cell – The cells will expand or even burst Types of Solutions • Isotonic Solutions- equal movement of water into and out of the cell – Equal concentration inside and outside the cell – Cells remain their normal size and shape Transport Proteins • Proteins stuck in the cell membrane act as transport tunnels that move substances into and out of the cell Ion Channels • Ion channels are transport proteins that move positive(+) and negative(-) ions across the cell membrane – Ex: Na+ and Cl- Gated Ion Channels • Gated Channels can open and close to allow or prevent ions from passing through Facilitated Diffusion • Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins to move substances across the cell membrane Carrier Proteins • How Carrier Proteins Work: – 1) Bind to a substance – 2) Change shape – 3) Release substance on other side of cell membrane Active Transport! • Active transport moves substances across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient, from low high • Active transport requires energy(ATP) Sodium-Potassium Pump • Transports sodium ions(Na+) out of the cell and transports potassium ions(K+) into the cell • Requires ATP(energy) as a form of active transport Movement in Vesicles • Cells use vesicles to transport large molecules into and out of the cell – Ex: glucose in & wastes out Endocytosis • The movement of large molecules into the cell • The cell engulfs the molecule Endocytosis Exocytosis • Movement of large molecules out of the cell • Cell releases the substance(waste) Exocytosis Endocytosis & Exocytosis END OF CHAPTER 4 NOTES!!!