* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System The master and
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
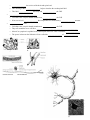
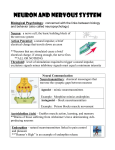
The Nervous System The master _________________ and _________________ system of the body Method of communication? _________________ impulses The Three Overlapping Functions It uses millions of sensory receptors to _________________ _________________ called _________________ inside and outside the body. It _________________ and _________________ this gathered information called _________________ input and makes decisions on what should be done. This process is called _________________. It _________________ a response by activating muscles or glands via _________________ output. Organization of the Nervous System _________________ Classification _________________ Nervous System (CNS) – _________________ and _________________ _________________. They _________________ incoming sensory information and issue _________________ in response _________________ Nervous System (PNS) – mainly _________________ that extend from the _________________ and act as _________________ lines. o _________________ nerves carry impulse to and from the spine o _________________ nerves carry impulse to and from the brain Functional Classification (PNS only) o _________________ or _________________ division – nerve fibers that carry impulses to the _________________ from sensory receptors _________________ sensory fibers come from the skin, skeletal muscles and joints _________________ sensory fibers or visceral afferents come from the visceral (_________________) organs o _________________ or _________________ division – go from Motor (efferent) _________________ to _________________ organs (_________________ and _________________) _________________ nervous system – the _________________ nervous system. Allows us to _________________ control skeletal muscles _________________ nervous system – the _________________ nervous system. Regulates events that need to be _________________ and has two complimentary parts called _________________ and _________________ Figure 7.2: Page 224 Cells of the Nervous System _________________ Also known as _________________ cells Highly specialized to _________________ messages from one part of the body to another The neuron has several important parts. _________________ _________________ o _________________ center of the neuron. o Contains the normal organelles except _________________. o The neuron’s shape is the result of the rough ER (called _________________ substance) and the intermediate filaments (called _________________) Armlike Processes or fibers o _________________ – many processes that carry information ______ the cell body o _________________ – the one process that carries information _________ from the body. The axon arises from the conelike region called the _____________ _________________. It may have an occasional _________________ branch (a split of the axon), but all axons branch _________________ at their ends. The Axon Terminals (Ends) o The end of the axon can branch _________________ or _________________ of times. Each branch is known as an _________________ _________________ o These contain hundreds of tiny vesicles that contain _________________. o When a signal reaches the end of the axon, the _________________ are released across the _________________ _________________ or _________________ (a space between the axon and the next cell) _________________ o A whitish, fatty material that covers nerve fibers o It helps _________________ and _________________ the transmission rate of nerve impulses Types of Supporting Cells - Known as _________________ (“nerve glue”) or ____________ or ____________ cells o _________________ o _________________ star-shaped cells (make up almost 50% of neutral tissue) o Their numerous projections have swollen ends that cling to neurons. They then _________________ and _________________ the neurons next to blood _________________. o They form a living barrier between the _________________ and the _________________ that keeps out _________________ materials from the blood. o o _________________ o o They also pick up extra _________________ and released _________________ Spiderlike _________________ that dispose of debris, including bacteria and dead brain cells _________________ Cells o o o _________________ the cavities of the brain and spinal cord. o Their beating of their _________________ helps to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. o This fluid _________________ the cavity and _________________ the CNS __________________________________ o Cells that create a myelin sheath around axons _________________ the CNS o It has several cell _________________ that wrap themselves around many _________________ neurons. _________________ cells o Cells that create a myelin sheath around axons _________________ the CNS o They roll around the nerve cell like a ___________________________________________________ o Most of its cytoplasm is squished to the outmost part of the cell. This is called the _________________ o The spaces in between the Schwann cells are called the _________________ of _________________ Interesting fact Most brain tumors are the result of _________________ cells forming the tumor. This is because neurons have lost their ability to _________________. This is also why _________________ damage can be so catastrophic for a person. Cluster Terms _________________ – well protected clusters of cell bodies in the CNS _________________ – small collections of cell bodies found outside the CNS _________________ – bundles of nerve fibers running through the CNS _________________ – bundles of nerve fibers running in the PNS _________________ matter – dense collection of myelinated fibers _________________ matter – contains mostly unmyelinated fibers Classification of Neurons Functional classification _________________ or _________________ – carry messages from sensory receptors to the CNS. Have dendrite endings associated with specialized receptors _________________ or _________________ – carry message to muscles or glands _________________ – connect the motor and sensory neurons in neutral pathways Structural _________________ neuron – most common type. It has several processes branching from the neuron _________________ – only has two processes, axon and a dendrite. _________________ – have a single process emerging from the cell body. But this process doesn’t go too far before it splits into a peripheral (distal, dendrite) and central (proximal, axon) branch