* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mathematical Practice Standards
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
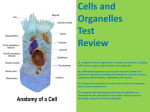
Name: Freda Vick & Esta Lampkin Lesson Plans Week of February 8-12, 2016 Monday February 8, 2016 Today’s Objectives: Teaching Strategies/ Activities: (Please be specific) Content Objective: Language Objective: (What you will do) (How you will do it—I Can. . .) The teacher will: Bellwork:What is the basic unit of all 1. provide students living things? with powerpoint on 1. Cell:s Structure and Function Cells Structure and powerpoint Function 2. Explain: “Compare the cell to a 2. have student l state Factory the structure and 3. Students can use this DE link to function of complete 2 for assistance. and functions of plant and animal unicellular and https://app.discoveryeducation.co cells, including major organelles multi-cellular m/learn/videos/9CAC5948(cell organisms. D76D-4EA4-9235membrane, cell wall, nucleus, 3. have students 3D5AFDB4870A?hasLocalHost= compare the chloroplasts, mitochondria, and false structures and life 4. Exit Ticket: Elaborate: Students vacuoles). functions of singleprovide reasoning why they chose 7.L.1.3 Summarize the celled organisms the organelles for each factory hierarchical organization of multithat carry out all the job. cellular organisms from cells to basic functions of tissues to organs to life including: systems to organisms. Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium, and Volvox Extra resource: http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Differentiation: Assessment: Evaluate: Do students know the functions of each Students use their own explanations to organelle? explain how the cell is like a factory. Standard: 7.1 Explain the processes, structures and functions of living organisms that enable them to survive, reproduce and carry out the basic functions of life. 7.L.1.2 Compare the structures x Literacy Strategies: Vocabulary Development Making predictions Produce and create Text analysis x Visualization Purpose setting x Collaboration Mathematical Practice Standards: Make sense of problem and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others x Comparisons with evidence Use appropriate tools, look for and make use of structure Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure Model with mathematics Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Tuesday February 9, 2016 Today’s Objectives: Content Objective: Language Objective: (What you will do) (How you will do it—I Can. . .) Standard: The teacher will: 1. provide students the DE video as a review 2. review the “Comparing the Cell to a factory” 3. use the strategy STIR: to collaborate learning and discussion See Monday’s Objectives Today’s Activities: (Please be specific) 1. Show the following videos in Resources:Discovery Ed Videos & cells alive website 2. Review “Comparing the Cell to a factory with justification. 3. STIR Strategy: Groups will be given an organelle on an index card, The group explains the function so that everyone explains. When prompted, 2 members move to another table and shares their organelle function with the other groups so that each table now has three organelles to discuss. Movement occurs again. http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Discovery education video resource https://app.discoveryducation.com/learn/videos/9CAC5948-D76D-4EA49235-3D5AFDB4870A?hasLocalHost=false Differentiation: Differentiation: Students can write, match or draw the function on the post-it note to give to teacher as they leave. x Assessment: Responses to the cell structure and function (verbal, written or drawn Literacy Strategies: Vocabulary Development Making predictions Produce and create Text analysis x Visualization Purpose setting x Collaboration Mathematical Practice Standards: Make sense of problem and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics x Comparisons with evidence Use appropriate tools, look for and make use of structure Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Wednesday FebruARY 10, 2016 Today’s Objectives: Content Objective: Language Objective: Today’s Activities: (Please be specific) (What you will do) (How you will do it—I Can. . .) Standands The teacher will 1. provide students a list of the six cell organelles for the strategy “Spend a Dollar” 2. provide the “Bounce Card” to use stem questions for inquiry when choosing how to “Spend a Dollar” See Monday’s Objectives Bellwork: What are the major functions of a cell that carry out life processes? Use the information from earlier in the week 1. Strategy: Spend a Dollar to show the importance of each organelle -cell membrane -nucleus -mitochondria -cell wall vacuoles -chloroplasts 2. Strategy: “Bounce Card” using stem 3 have students to questions for inquiry when choosing how complete “Comparing a Cell to “Spend a Dollar” 3. Complete “Comparing a Cell to a to a Factory” (use Factory” (use modified from A Busy modified from A Factory,website: Busy Factory, http://www.beyondbooks.com/lif71/4a.asp website:http://www 4 Complete previous assignments .beyondbooks.com/l 5 Notebook Check if71/4a.asp) 4 Complete assignment from previous assignments5 Notebook Check Comparing a Cell to a Factory use modified from A Busy Factory, website: http://www.beyondbooks.com/lif71/4a.asp Differentiation: x x Literacy Strategies: Vocabulary Development Making predictions Produce and create Text analysis Visualization Purpose setting Collaboration Mathematical Practice Standards: Make sense of problem and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the x Comparisons with evidence Use appropriate tools, look for and make use of structure Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure reasoning of others Model with mathematics Thursday Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning February 11, 2016 Today’s Objectives: Today’s Activities: Content Objective: Language Objective: (Please be specific) Standard: Teacher will have students to explain that both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body and vacuoles. Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts 1. Engage: Ask the students the following (What you will do) See Monday’s Objectives (How you will do it—I Can. . .) questions: -How do you get energy? (eating food, using your mouth) -How does your body protect itself from unwanted things entering or exiting the body? (your skin) -What part of your body is like a control center (your brain) Explain how your cells also have life functions: -the cell wall and cell membrane is like your skin -the nucleus is like your brain -the chloroplasts make food for plants (like you make food for yourself) -the mitochondria release energy -the vacuoles store water (like you fill a water bottle) 2. Explore: Show the following videos in Discovery Ed. -cell membrane -nucleus -mitochondria -cell wall and vacuoles -chloroplasts 3. Explain: Use the Cells Alive website to guide your lesson on the cell parts. You only need to focus on the 6 cell parts. 4. Elaborate: Have students complete a "Cell is like a…" project. (1,2,8) 5. Evaluate: How well students can relate cell parts to factory parts and Review Cardst Differentiation: x Literacy Strategies: Vocabulary Development Produce and create x Assessment: Making predictions x Text analysis Visualization Purpose setting Collaboration Comparisons with evidence Mathematical Practice Standards: Make sense of problem and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Use appropriate tools, look for and make use of structure Attend to precision Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics Look for and make use of structure Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Friday February 12, 2016 Today’s Objectives: Content Objective: Language Objective: (What you will do) (How you will do it—I Can. . .) Standard: The teacher will present students an opportunity to analyze a text. See Monday’s Objectives Differentiation: Students will highlight important points from the reading passage. x Literacy Strategies: Vocabulary Development Produce and create Collaboration Mathematical Practice Standards: Make sense of problem and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics Special Notes:DPI unpacked Content Bellwork: 1. Strategy: First Turn/Last Turn - analyze the text from newsela Title: The leafy green sea slug https://newsela.com/articles/banditseaslugs/id/12877/ ( 1st Turn, Last Turn: a.students read a passage, highlight key points.he owner then b. students share the sentence with the group ONLY. 3. Each member of the team explains why they think the person chose the passage in sequence. 4. The owner then states their reasoning why they chose the passage. 5. The next person repeats steps 1-4, This continues until all members have taken a turn.) Assessment: Complete review questions for comprehension x x Visualization x Today’s Activities: (Please be specific) Making predictions Text analysis Purpose setting x Comparisons with evidence Use appropriate tools, look for and make use of structure Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning 7.1.1 Within cells, many of the basic functions of organisms-such as extracting energy from food, getting rid of waste, movement and secreting waste-are carried out. The way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms. Even the simplest organisms have parts which enable them to move, take in food, to reproduce and to detect the environment they are in. Euglena-moves by a flagellum, know for a unique feature-- an eye spot, some contain chlorophyll and are common in fresh water. The amoeba moves by cytoplasmic streaming, surrounds food and engulfs it using pseudo pods. Paramecium is the most complex and specialized of the Protists. It moves by cilia. Volvox is a colony of ciliates, some containing chlorophyll. 7.L.1.2 All living things are composed of cells, from just one to many millions, whose details usually are visible only through a microscope. A cell is the smallest part of any living thing. There are many parts of a cell. Each part of a cell completes a certain function for the cell. These parts are found in plant and animal cells. • Cell Membrane - forms the outer boundary of the cell and allows only certain materials to move into or out of the cell • Cytoplasm - a gel-like material inside the cell; it contains water and nutrients for the cell • Nucleus - directs the activity of a cell; it contains chromosomes with the DNA • Nuclear Membrane - separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Mitochondria - break down food and release energy to the cell • Vacuoles - are storage areas for the cell Some organelles are found only in Plant cells. These organelles are: • Cell Wall - provides structure to the plant cell • Chloroplasts - contain chlorophyll that is make food for the plant cell. 7.L.1.3 Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, whole organisms and ecosystems. Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. Groups of specialized cells cooperate to form a tissue, such as muscle. Different tissues are in turn grouped together to form larger functional units, called organs. Organs group together to form systems and systems group together to form organisms. Each type of cell, tissue, organ, organ system has a distinct structure and functions that serve the organism as a whole. Essential Vocabulary Protists Cilia Pseudopod Volvox Amoeba Autotroph Heterotroph Flagellum Paramecium Euglena Cells cell membrane cell wall chloroplasts mitochondria cytoplasm, nucleus nuclear membrane golgi bodies endoplasmic reticulum vacuoles