* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (5 points).
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
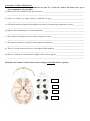
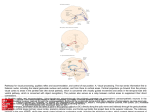
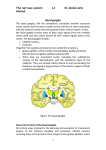
Pázmány Péter Catholic University Faculty of Information Technology and Bionics Department of Neuroscience INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Exam 2nd June 2015 Name: ....................................................................... Points: 100 / .............................................................. Signature of examiner ............................................................. Signature of examinee (Sign upon acceptance of correction) NEURONAL MORPHOLOGY AND FUNCTION (5 POINTS). Define briefly the following terms. a) Asymmetric mytosis:__________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ b) Equilibrium potential:_________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ c) Membrane time constant:______________________________________________________________ d) Spike timing dependent plasticity:_______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) Tetanus:____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ NEURONAL NETWORK OPERATION (5 POINTS). Define the following terms. a) Local field potential (LFP):_____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ b) Central pattern generator:______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ c) Members of the thalamocortical circuit:_________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Sensory binding:______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) Sharp wave-ripple complex:_____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ SENSORY SYSTEMS (10 POINTS). A) Decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F), and by the latter case, give a short explanation, why (8 points). a) Mitral cells in the olfactory bulb possess axons.______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ b) Odors are coded by a single olfactory epithelial cell type.____________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) ON bipolar neurons depolarise through the activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors.____________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Bipolar cells communicate by action potentials.______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) The parietal visual pathway ensures the perception of action. ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ f) The aperture problem is solved by inferotemporal visual areas.__________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ g) There is overlap between the parvo- and magnocellular pathway.________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ h) Illusoric contours are first detected in higher order cortical regions. ______________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ B) Render the numbers of dissections to the resulting visual field defects (2 points). THE MOTOR SYSTEM (30 POINTS). A) THE OLIVOCEREBELLAR MODULE. Name the cell types and anatomical structures (assigned by numbers) and render them to the statements below. (15 points) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 4. 5. 3. 5. 2. a) It is responsible for the cerebellar feedback inhibition. _______ b) Postinhibitory rebound can be observed in this cell type. _______ c) The output of the cerebellum is established by this cell type. _______ d) Climbing fibers are axons originating from this cell type. _______ e) Inhibitory cell type in the cerebellum. _______ f) Its function is to read out the output of the motor cortex. _______ g) It is innervated by parallel fibers. _______ h) Complex spikes are generated in this cell type. _______ i) Members of this cell type are coupled by gap junctions. _______ j) It has oscillatory activity. _______ B) BASAL GANGLIA. Supplement the text. (10 points) The main neurotransmitter of basal ganglia (=BG) neurons is _________________________. The only glutamatergic element of the BG is the ___________________________. Source of dopamine is the _________________________________________________. The role of dopamine in the BG is e.g. _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________. The interaction between glutamate and dopamine applies equally to the cortical and _______________________ inputs. In human, the main output element of the BG is the _____________________________. Elements of the direct pathway can be found in the so-called____________________. The indirect pathway of the BG is the following: ___________________________________________________________. Overactivation of the indirect pathway leads to the ______________________ of basal ganglia targets. Activation of the direct pathway leads to the _________________________ of basal ganglia targets, e.g. (add at least two)_______________________________________________. C) UPPER MOTOR STRUCTURES. a) Identify the assigned cortical regions in the following figure (2 points). 1. 2. 3. 4. b) Give the name of a cortical brain region or tract to the following properties and motor functions. (8 points) a) The most important executive motor pathway: b) A so-called homunculus can be derived from its receptive field: c) It is responsible for the integration of emotion induced motions: d) Muscle tone is regulated by it: e) Mental rehearsal of motor tasks: f) Informing the other motor structures about the planned movement: g) Preparing the next motion response: h) Transfer of sensory information originating from motions to the primary motor cortex: LEARNING, MEMORY, EPILEPSY. (10 POINTS) A) Assign cell types to the letters in the figure depicting hippocampal firing patterns, then answer the questions. (5 points) D E A: B: A C: D: A E: valley phase A B C a) Name the depicted oscillation (name + frequency range): ____________________________ b) Define the role of the firing pattern represented by C._______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Define the significance of the oscillation phases depicted by E.________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ B) EPILEPSY. (5 points) a) Give two underlying reasons for epileptic seizures.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Give at least two functional and morphological changes of the neuronal network accompanying epilepsy. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Define the main electrophysiological difference between partial and generalized seizures._____________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Describe briefly the loop of epileptic network reorganization. ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) Give at least two cell types which is reduced in number due to epilepsy.___________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS, BEHAVIOUR (10 POINTS). A) ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS. Underline the correct phrases. (5 points) a) Portal circuitry of the hypophysis is established in pars tuberalis / median eminence. b) Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus / supraoptic nucleus,… c) … and released to the blood in the posterior / anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. d) Secretion of thyroid hormones is indirectly induced by CRH / TRH. e) Hormones secreted by the gonads are proteins / lipids. f) Hormone molecules attach to ionotrop receptors / metabotrop receptors. g) There is feedback mechanism in two levels / three levels along the hypothalamus-target organ axis. h) Hypophysiotrophic neurons can be found in one single / several hypothalamic nucleus/nuclei. i) TRH is a parvicellular / magnocellular hormone. j) Stomatostatin induces / inhibits growth. B) BEHAVIOUR. (5points) a) Add at least two main characteristics of the behavioural responses leading to psychiatric diseases.______ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Give at least two main neuromodulators contributing to psychiatrical diseases. _____________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Add at least one factor which ensures that psychiatrical diseases can be modelled in animals.__________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Add the two main types of psychotherapy. __________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) Define briefly what is the Papez circuit._____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ EXPERIMENTAL APPROACHES (10 POINTS). A) What kind of method would you apply to … a) model natural aggression in animal________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ b) examine the default mode network: _______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) inhibit a particular cell type in a reversible manner ___________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) examine the presence of a particular hormone receptor on a cell_________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) detect ‘face selective’ visual brain region___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ f) induce fear directly_____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ B) OPTOGENETICS. a) Add at least two advantages of optogenetics over electrical stimulation and pharmacological treatment. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Describe what ensures the specificity of opsin expression in target brain areas. _____________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Add at least two ways optogenetics can modulate cell function. _________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Give at least two technical and ethical problems of potential optogenetical applications in human. ______ ____________________________________________________________________________________ DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES (15 POINTS). A) Render the diseases to the statements and symptoms (multiple choice is possible). P = Parkinson’s disease C = cerebellar disease P = impairment of the pyramidal path N = none a) It involves essential tremor. _______ b) It involves resting tremor. _______ c) It induces cognitive disturbances. _______ d) Deep brain stimulation is applied in its treatment. _______ e) It can induce nystagmus. _______ f) Patients are paretic. _______ g) It involves pathological reflexes. _______ h) Speech can be impaired. _______ i) It can be genetically determined. _______ B) Write in detail what diagnostic or therapeutic method can be applied to … (6 points) a) treat anxiety (pharmacon)________________________________________________________________ b) treat drug-resistant epilepsy: _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ c) demonstrate cognitive disturbance in Parkinson’s disease: ______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ d) direct a robotic arm: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ e) partially restore the function of motor cortex after stroke injury__________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ f) restore the function of damaged photoreceptors: _____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________