* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA * History, Structure, and Functions
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
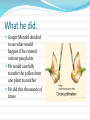
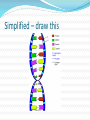
The History Born in 1822 Gregor Mendel eventually became the “Father of Genetics” Friar Scientist What he did. Gregor Mendel decided to see what would happen if he crossed various pea plants He would carefully transfer the pollen from one plant to another He did this thousands of times The Traits he tested. His work and others led to… Dominant only shows when present Dominant does not mean better Recessive does not mean worse Some definitions and facts Homozygous - genotype with the same alleles. For example: RR, or rr Heterozygous - genotype with the different alleles. For example: Rr. There are 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in a normal human cell - diploid There are 23 chromosomes in a gamete (sex cell) - haploid Mitosis takes 1 body cell (diploid) and makes 2 identical body cells (diploid) Meiosis – finishes with 4 similar haploid cells (23 chromosomes Homozygous and Heterozygous Phenotypes and Genotypes Genotypes = the genetic code (on the inside) Phenotypes = the physical characteristics (on the outside) Phenotype vs Genotype What makes up DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid Simplified – draw this Structure - continued Purines – Adenine and Guanine. These are the larger of the 2 types of DNA bases Pyrimidines – Thymine and Cytosine. Smaller type of DNA base DNA Replication - Definition In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA Replication