* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant and Animal Cell Foldable
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
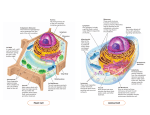
Plant and Animal Cell Foldable Step 1: Holding an 8 1/2" x 11" paper horizontally, fold both ends in so they meet, but do not overlap. The plant and animal cell drawing should be on the front of the left and right side. See teacher example. Step 2: Label, Number and Color the Parts of the Cell Use this sheet as a checklist to make sure that you have included all the required information in your foldable. 1 . Front Cover: Left side: Plant Cell Label, number, and color the following structures: Cell Wall (Dark Green) Cell Membrane (Dark Blue) Chloroplasts (Green) Nucleus Cytoplasm (Yellow) Nucleolus Ribosomes Vacuole DNA/Chromatin Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough E.R.) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth E.R.) Right side: Animal Cell Label, number, and color the following structures: Mitochondria Cell Membrane (Dark Blue) Cytoplasm (Light Blue) Nucleus Ribosomes Nucleolus DNA/Chromatin Vacuole Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough E.R.) Lysosome Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth E.R.) RIGHT SIDE, Pg - 1 1 . Inside the Foldable: Step 3: Inside the Left Side (Under the Plant Cell): ● Left side: Plant Cell List and define the 3 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in plant cells. 1. Cell Wall 2. Chloroplast 3. Vacuole Step 4: Inside the Right Side (Under the Animal Cell): ● Right side: Animal Cells List and define the 2 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in animal cells. 1. Lysosome 2. Vacuole Step 5: Center Panel (under both flaps): ● Center: Plant and Animal Cells ● Create a simile for the 8 organelles found in both Plant and Animal Cells. ○ Each component would play a role in the simile and should explain its function/job inside the cell. ○ Include a picture of your similie with each cell part. ○ Example: The Cell is like a_____ …. ■ the nucleus acts like the …. _________ 1. Cell Membrane 2. Chromatin /DNA 3. Cytoplasm 4. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 5. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 6. Mitochondria 7. Nucleus 8. Ribosomes ● Now go back and do the same thing for the organelles found only in the plants and animal cells on the interior side flaps. (Cell wall, etc.) RIGHT SIDE, Pg - 2 Organelle Structure & Function CELL STRUCTURE Cell Wall Cell Membrane LOCATION Plant, Fungi, & Bacteria, but not animal cells DESCRIPTION ● ● ● Outer layer Rigid & strong Made of cellulose ● Plant - inside cell wall Animal - outer layer; Double layer of phospholipids with proteins Selectively permeable ● All cells ● Nucleus Nuclear membrane Cytoplasm All cells except prokaryotes ● ● ● ● All cells except bacteria All cells Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) All cells except bacteria Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) All cells except bacteria ● ● Large, oval Contains 1 or more nucleoli Holds DNA Surrounds nucleus Double membrane Selectively permeable ● Clear, thick, jelly like material (cytosol) ● Network of tubes or membranes embedded with ribosomes ● Network of tubes or membranes w/o ribosomes FUNCTION ● ● ● Support (grow tall) Protection allows H O, O , CO to 2 2 2 diffuse in & out of cell ● ● ● Support Protection Controls movement of materials in/out of cell Barrier between cell and its environment Maintains homeostasis ● ● ● ● Controls cell activities Contains the hereditary material of the cell ● Controls movement of materials in/out of nucleus ● Supports and protects cell organelles ● Aids in making proteins ● Aids in making lipids RIGHT SIDE, Pg - 3 CELL STRUCTURE Ribosomes Mitochondria Vacuole Lysosome LOCATION DESCRIPTION ● All cells All cells except bacteria Plant cells have a single, large vacuole Animal cells have many small vacuoles Plant - uncommon Animal - common ● ● ● Nucleolus Fluid-filled sacs Largest organelle in plant cells ● Small and round with a single membrane Plants and algae ● All cells except prokaryotes Peanut shaped Double membrane ● ● ● Chloroplast Small bodies free or attached to rough ER Made of rRNA & protein ● ● Green, oval containing chlorophyll (green pig Found inside the cell's nucleus May have more than one Disappear during cell division FUNCTION ● Synthesizes (makes) proteins ● Breaks down sugar (glucose) molecules to release energy Site of cellular respiration ● ● ● ● ● ● Store food, water, metabolic and toxic wastes in all cells Store large amounts of food or sugars in plants Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules Digests old cell parts ● Uses energy from sun to make food (glucose) for the plant Process called photosynthesis Release oxygen ● Make ribosomes ● RIGHT SIDE, Pg - 4