* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Huffman PowerPoint Slides
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Psychologist wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
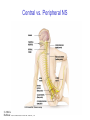
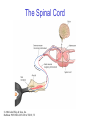
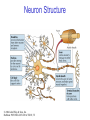
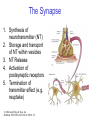
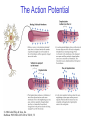
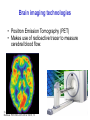
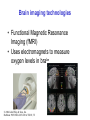
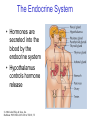
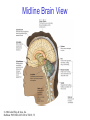
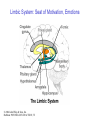
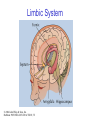
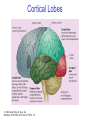
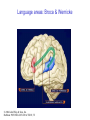
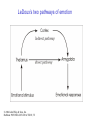
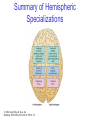
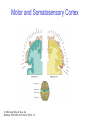
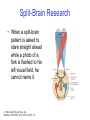
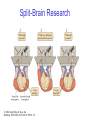
The Nervous System © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Central vs. Peripheral NS © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Central Nervous System • The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord • Spinal cord connects the brain with the PNS – Spinal cord is comprised of cell bodies and axons that carry messages • Afferent: toward the brain (sensory function) • Efferent: away from the brain (motor function) © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Peripheral Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) includes all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord – Somatic NS carries sensory messages to brain and motor commands to the muscles – Autonomic NS regulates automatic body functions (such as heart rate, breathing) • Sympathetic: “Fight or Flight” • Parasympathetic: dominant when relaxed © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Autonomic Nervous System © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Spinal Cord © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Neurons • Neurons are cells that transmit information • Neurons are composed of: – Dendrites: receive information and pass it to cell body – Cell Body: summarizes information – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Neuron Structure © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Synapse © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Synapse • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite or cell body. • Neurotransmitter (NT) molecules are released from the axon terminal into the synapse when the action potential arrives at the axon terminal. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Synapse 1. Synthesis of neurotransmitter (NT) 2. Storage and transport of NT within vesicles 3. NT Release 4. Activation of postsynaptic receptors 5. Termination of transmitter effect (e.g. reuptake) © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Resting Potential Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Action Potential • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit the axon © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Action Potential © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Action Potential Details • Action potentials vary in frequency (a few pulses per second to a max of 1000 pulses per second) • APs have a refractory period (about 1 msec) • AP is “all or none” in nature © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Myelin • Myelin is a fatty, waxy substance coating the axon of some neurons. • Functions: – Speeds neurotransmission – Insulates neurons from each other – Makes neurotransmission more efficient © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Brain imaging technologies • Positron Emission Tomography (PET) • Makes use of radioactive tracer to measure cerebral blood flow. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Brain imaging technologies • Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) • Uses electromagnets to measure oxygen levels in brain. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Neurotransmitters • • • • • • • Serotonin Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine Epinephrine GABA Endorphins © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Psychoactive Drugs • Psychoactive drugs affect the nervous system to alter mood, emotion, and thought • Psychoactive drugs act by: – Increasing or decreasing release of neurotransmitters – Stimulating or blocking receptor sites © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Psychoactive Drugs • Agonists enhance neurotransmitter function • Antagonists block neurotransmitter function © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Endocrine System • Hormones are secreted into the blood by the endocrine system • Hypothalamus controls hormone release © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E The Endocrine System Functions of the endocrine system: 1. Maintain homeostasis 2. Regulate reproductive system © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Midline Brain View © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Brainstem • Brainstem is a primitive portion of brain – Pons: involved in respiration, sleep regulation, dreaming – Medulla: involved in life support functions such as respiration and heart rate – Reticular activating system is an arousal system within the brainstem © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Subcortical Brain Areas • Corpus callosum: band of axons that interconnects the hemispheres • Thalamus: sensory relay area • Limbic system: involved in emotionality • Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, fighting, homeostasis • Cerebellum: involved in motor control © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Limbic System: Seat of Motivation, Emotions © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Limbic System © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Cerebral Cortex • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension – Localization of function: do discrete circuits carry out different functions? © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Cortical Lobes © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Language areas: Broca & Wernicke © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E LeDoux’s two pathways of emotion © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Summary of Hemispheric Specializations © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Motor and Somatosensory Cortex © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Split-Brain Research • When a split-brain patient is asked to stare straight ahead while a photo of a fork is flashed to his left visual field, he cannot name it. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Split-Brain Research © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Behavioral Genetics • Behavioral genetics examines the influence of genes (versus environment) on behavior • Research strategies: – Twin studies: compare the concordance (agreement) rates between identical and fraternal twins – Adoption studies: compare the similarity between adopted children and their biological/adopted parents – Mutations: examine behaviors in genetically abnormal subjects or in animals in which a specific gene has been “knocked out” © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Evolutionary Psychology • Darwin argued that natural forces select traits that are adaptive for survival – Natural selection: certain traits are passed on because these traits gave an advantage for survival • Organisms with these traits are able to reproduce and pass on the trait to their offspring – Genetic mutations can be beneficial or disastrous • Evolutionary psychology examines how evolutionary processes impact behavior © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E Copyright Copyright 2004 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission of the copyright owner. © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman: PSYCHOLOGY IN ACTION, 7E