* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7A- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis - TJ
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
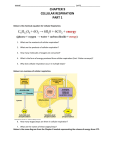
Name Date Period Chapter 7A- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis The below figure introduces the 3 stages of cellular respiration. Label the diagram. Include electron transport chain, pyruvate, mitochondrion, citric acid cycle, glycolysis, cytoplasm, glucose, 2 NADH, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 34 ATP, 38 ATP. 1 Glycolysis is the first of 3 steps in cellular respiration. Review glycolysis by matching each phrase on the left with a term on the right. Some terms are used twice, some questions may have more than 1 answer. 1. Compound formed as glucose is changed to pyruvic acid. A. NADH 2. Molecule broken down in glycolysis B. Pyruvate 3. Invested to break apart glucose molecule at start of process C. ATP 4. Glucose is converted to two molecules of this D. NAD+ 5. “Splitting of sugar” E. Glucose 6. Carries hydrogen and electrons from breakdown of glucose F. Glycolysis 7. What is the role of NAD+ & FAD+2 in cellular respiration? 8. Glycolysis starts with and produces 9. Write the summary equation for cellular respiration: a. Where did the glucose come from? b. Where did the O2 come from? c. Where did the CO2 come from? d. Where did the H2O come from? e. Where did the ATP come from? 10. STAGE 1: Glycolysis a. Occurs where? b. Starts with? c. Produces? d. Yields how much ATP directly? 11. Why is glycolysis thought to be one of the earliest of all biochemical processes to have evolved? 2 Select the best answer. 12. Which of the following describes glycolysis? a. b. c. d. e. It begins the breakdown of glucose It produces a small amount of ATP It generates NADH It splits glucose to form two molecules of pyruvate All of the above 13. As a result of glycolysis there is a net gain of a. 2 b. 4 c. 36 d. 0 ATPs. e. 1 14. Which of the following is a result of glycolysis? a. b. c. d. e. production of CO2 conversion of FAD2+ to FADH2 conversion of NADH to NAD+ a net loss of two ATPs per glucose molecule conversion of glucose to two pyruvates 15. When cells break down food molecules, energy a. b. c. d. is released all at once. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 16. A substance produced during photosynthesis that is used for completion of cellular respiration is a. water. c. NADPH. b. ATP. d. oxygen. 17. When glycolysis occurs, a. a molecule of glucose is split. b. two molecules of pyruvic acid are made. c. some ATP is produced. d. All of the above 3