* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-cell-cycle-and-division-mitosis-16-17
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
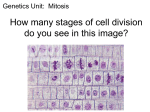
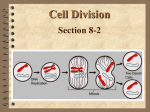
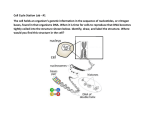
Cell Growth and Division Biology Ms. Lew Vocabulary (p. 90-91) • • • • • • • Cell Cycle Chromatin Chromosome DNA overload Interphase Sister Chromatid Spindle Fiber What is the cell cycle? • During the cell cycle, a “parent” cell grows and divides to form 2 “daughter” cells. • The cycle has three main stages –Interphase –Mitosis –Cytokinesis Remember the two reasons why cells divide rather than continue to grow larger: DNA Overload 1. __________________________________ Exchanging Materials 2. _________________________________ DNA overload is when the DNA has too many tasks to do (such as making proteins) and not enough DNA to get the job done efficiently. The Cell Cycle • Animation G1 M G2 S Interphase – G1 , S & G2 • During Interphase cells: – G1 phase: Grow to mature size • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are duplicated – S phase: Replicate (copy) DNA – G2 phase: Prepare for cell division • Cell grows • Most of a cells life is spent in Interphase. Chromosomes • Are made of DNA, histones, chromatin • Each chromosome consists of sister chromatids attached at a centromere • Each sister chromatid is an exact copy Mitosis – M phase • The cells nucleus divides into two nuclei • There are four phases – – – – Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase P M A T Animal Cell Mitosis- Video Prophase • 1st stage of Mitosis • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes • Centrioles separate and a spindle fiber begins to form. • Nuclear membrane breaks down Prophase Metaphase • 2nd Phase of Mitosis • Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. • Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber. Metaphase Anaphase • 3rd Phase of Mitosis • The sister chromatids separate at the centromere and move to opposite ends of the cell. Anaphase Telophase • 4th Stage of Mitosis • Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cells and lose their shapes (return to chromatin form) • Two new nuclear membranes form, one for each cell. Telophase Cytokinesis • The cytoplasm pinches in half. • Each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes Cytokinesis Overview sim • http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/a nimations/content/mitosis.html Plant cell mitosis • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aDAw2 Zg4IgE And Another one… • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KzBoI AMVUSY