* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alu
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
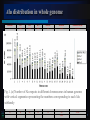
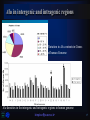
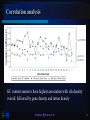
IRPB Analysis of Alu repeat elements Pusan National University Interdisciplinary Research Program of Bioinformatics Molecular biology & Phylogeny Laboratory Woo-Yeon Kim [email protected] 1 CONTENTS Whole-genome analysis of Alu repeat elements reveals complex evolutionary history INTRODUCTION NEW IDEAS RESULTS DISCUSSIONS Alu repeat analysis in the complete human genome: trends and variations with respect to genomic composition [email protected] 2 Genome Research - Letter Supplemental material is available online at www.genome.org [email protected] 3 INTRODUCTION [email protected] 4 Alu repeats A family of SINEs, short interspersed nuclear elements Replicating via LINE-mediated reverse transcription of an RNA polymerase Ⅲ transcript Roughly 280 bp The history of substitution patterns in the human genome Markers to determine genetic distances between human subpopulations – polymorphic Alu insertions L Poly A signal AAAAA R Poly A signal AAAAA SINE Structure [email protected] 5 K-means Place K points into the space represented by the objects that are being clustered. These points represent initial group centroids. Assign each object to the group that has the closest centroid. When all objects have been assigned, recalculate the positions of the K centroids. Repeat Steps 2 and 3 until the centroids no longer move. This produces a separation of the objects into groups from which the metric to be minimized can be calculated. [email protected] 6 NEW IDEAS [email protected] 7 An example using real data Only the 5 Alu positions with diagnostic mutations in the Ya5 subfamily (position 91, 98, 146, 175, and 238) Applying k-means clustering, k = 2 [email protected] 8 Looking for overrepresented pairs Identifying nested subfamilies Computing biprofiles, frequencies of pairs of nucleotide values [email protected] 9 RESULTS [email protected] 10 Aligned consensus sequences of selected subfamilies Roughly 480,000 full-length Alu elements Recursively split subfamilies Identifying 213 subfamilies [email protected] 11 An evolutionary tree of Alu subfamilies [email protected] 12 DISCUSSION Significant mutation from the consensus sequence Available detected by a rigorous whole-genome analysis Partial results Not statistically discernible Limitations in this algorithm Limitations – Excluding Insertion/deletion mutations Frequent CpG mutations Mutations to nucleotide values already present in other subfamilies Statistically distinguishable subfamilies Only 19 of the 31 subfamilies currently reported in Repbase Update [email protected] 13 Bioinformatics – Discovery Note Online Supplementary data is available at the web page www.igib.res.in/manuscriptdata/aluanalysis.html [email protected] 14 Alu distribution in whole genome Chromosome Alu J Alu S Alu Y Other Alus Total Alu No. Chromosome Size (bp) 1 25043 56044 12209 8114 101410 221782893 2 19679 46673 11295 6438 84085 237637456 3 15812 37539 9135 5044 67530 194846173 4 12857 30347 8158 4242 55604 188402715 5 12932 32423 8023 4351 57729 177705559 6 14449 35722 8375 4959 63505 175762617 7 17486 38816 8277 5150 69729 153794793 8 12092 27148 6203 3825 49268 142788062 9 10741 26910 6496 3441 47588 117013362 10 13909 31110 6707 4378 56104 131098977 11 11858 27461 6357 3744 49420 133239679 12 14932 32314 7026 4718 58990 129362603 13 6467 15929 4307 2114 28817 95228136 14 8921 20201 4392 2931 36445 88182284 15 9631 22169 5284 3000 40084 83582680 16 13913 29451 5462 3864 52690 80889146 17 13542 34653 7025 4150 59370 80734148 18 5935 13285 3333 1915 24468 74619305 Fig.1. (a) Number of Alu repeats in different chromosomes in human genome with vertical segments representing the numbers corresponding to each Alu subfamily 19 14135 34297 6130 3912 58474 56446152 20 7245 16478 3058 2236 29017 59424940 21 2681 6965 1865 752 12263 33917895 22 5378 13590 3119 1586 23673 33821705 X 11160 25841 5405 3284 45690 147274156 Y 1699 3547 1128 465 6839 22660226 Un 86 226 68 39 419 1374146 [email protected] 1179211 15 Alu repeat density and association with genes Fig. 1. (b) Variation in Alu and gene densities in human genome [email protected] 16 Alu in intergenic and intragenic regions Variation in Alu contents in Genes of human Genome Alu densities in the intergenic and intragenic regions in human genome [email protected] 17 Distribution of Alu subfamilies The most abundant Alu subfamily – Alu S, 6.4 % region of the genome Chromosome Y The most Alu poor chromosome High density Alu Y – very low density Alu S, Alu J Chromosome 13, 9 – similar trend 13 having least density of Alu J Chromosome 8, X High density Alu S, J Very low density Alu Y [email protected] 18 Correlation analysis GC content seems to have highest association with Alu density overall, followed by gene density and intron density [email protected] 19 DISCUSSION Analysis of Alu distribution in genes Statistically significant correlation between Alu and gene densities A higher Alu density in intragenic regions – These elements are preferred in genes. The highest Alu and gene densities – Chromosome 19, 22 Alu density is correlated in the order GC content > gene density > intron density The abundance of Alu subfamilies – Alu S > Alu J > Alu Y Young subfamilies - Chromosome 9, 13 and Y Old subfamilies – Chromosome 8 and X Higher correlation of older Alus with GC content than younger ones [email protected] 20