* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription and Translation Eukaryotic Cell
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
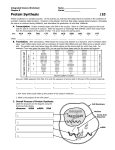
Transcription and Translation Eukaryotic Cell- A cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other membrane-enclose organelles (protists, plants, animals, and fungi). Nucleus- The chromosome containing organelle of a eukaryotic cell. DNA is located in the nucleus, transcription and mRNA processing occurs in the Nucleus. Codon- Specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; basic unit of genetic code. Ribosomes- Organelle constructed in the nucleolus and functioning as the site of protein synthesis. They control the coupling of tRNA molecules to mRNA codons. Nucleotide- Five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and phosphate group. Amino Acid- Organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Serve as monomers of proteins. mRNA- is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides, each of which contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It carries genetic information from the gene (DNA) out of the nucleus, into the cytoplasm of the cell where translation occurs to produce a protein. tRNA- functions to transport amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis rRNA- a structural component of the ribosomes. Proteins are very important in determining the characteristics of our bodies. - The instructions for making a protein are provided by a gene. A Gene is a specific segment of a DNA molecule. A gene contains sequences of nucleotides; this specifies which sequence of amino acids should be joined to form a protein. The sequence of amino acids in the protein determines the function and structure of that protein. A gene directs the synthesis of a protein by a two-step process - Transcription - is the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template. -When the mRNA is synthesized, RNA nucleotides are added, and each RNA nucleotide is matched to the DNA nucleotide in the gene. This nucleotide matching follows a base-pairing ruleComplementary nucleotides for base-pairing between two strands of DNA Complementary nucleotides for base-pairing between DNA and RNA G (guanine) pairs with C (cytosine). G pairs with C. A (adenine) pairs with T (thymine). A in DNA pairs with U (uracil) in RNA. T in DNA pairs with A in RNA. -Translation - The process where ribosomes synthesize proteins using the mature mRNA transcript produced during transcription First Base U C A G Genetic Code Second Base Third Base U C A G UUU phenylalanine UCU serine UAU tyrosine UGU cysteine U UUC phenylalanine UCC serine UAC tyrosine UGC cysteine C UUA leucine UCA serine UAA stop UGA stop A UUG leucine UCG serine UAG stop UGG tryptophan G CUU leucine CCU proline CAU histidine CGU arginine U CUC leucine CCC proline CAC histidine CGC arginine C CUA leucine CCA CAA proline glutamine CGA arginine A CUG leucine CCG CAG proline glutamine CGG arginine G AUU isoleucine ACU AAU threonine asparagine AGU serine U AUC isoleucine ACC AAC threonine asparagine AGC serine C AUA isoleucine ACA threonine AAA lysine AGA arginine A AUG (start) ACG methionine threonine AAG lysine AGG arginine G GUU valine GCU alanine GAU aspartate GGU glycine U GUC valine GCC alanine GAC aspartate GGC glycine C GUA valine GCA GAA alanine glutamate GGA glycine A GUG valine GCG GAG alanine glutamate GGG glycine G