* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
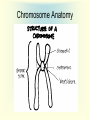
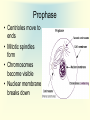
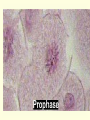
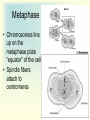
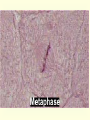
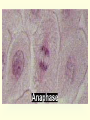
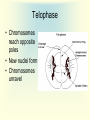
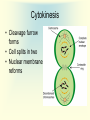
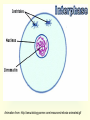
Cell Growth and Mitosis Cell Growth • Organisms grow by producing more cells • Cell division occurs throughout an organisms life • Why do cells divide instead of just getting bigger? – Large cell = harder to move substances in and out – High Surface to Volume ratio Surface/Volume • S/V is the ratio of surface area to internal volume • A smaller S/V is more efficient for moving substances in and out of a cell • Cells stay small and divide to be more efficient Cell Cycle • Time from the beginning of one division to the beginning of the next Cell Cycle • G1 phase – cell growth occurs • S phase – DNA replication • G2 phase – cell prepares for division, special organelles produced • M phase – cell division occurs • G1, S, G2 are known as INTERPHASE Mitosis • Cells divide in a series of recognizable stages known as mitosis • Interphase (cell growth stage) – Prophase – Metaphase – Anaphase – Telophase – Cytokinesis Cell Division Chromosome Anatomy Prophase • Centrioles move to ends • Mitotic spindles form • Chromosomes become visible • Nuclear membrane breaks down Metaphase • Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate “equator” of the cell • Spindle fibers attach to centromeres Anaphase • Chromatids begin to pull apart • Sister chromatids begin moving to opposite ends of cell Telophase • Chromosomes reach opposite poles • New nuclei form • Chromosomes unravel Cytokinesis • Cleavage furrow forms • Cell splits in two • Nuclear membrane reforms Animation from: http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/mitosis-animated.gif