* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Engineering (and other cool molecular biology techniques)
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
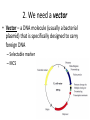
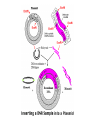
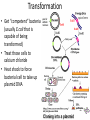
Genetic Engineering (and other cool molecular biology techniques) DNA Cloning • DNA cloning permits production of multiple copies of one particular gene • This gene copy will be used to produce a usable protein product (e.g. insulin) or for genetic engineering (e.g. gene for pest control inserted into plant) For Fun: • We want to clone a gene that produces a protein that will help you focus while studying. 1. We need the gene • This gene is located on chromosome 16 2. We need a vector • Vector – a DNA molecule (usually a bacterial plasmid) that is specifically designed to carry foreign DNA – Selectable marker – MCS 3. Restriction Enzymes • Restriction Enzymes – cut DNA at particular sequences – Ex: EcoR1 – recognizes GAATTC – 100’s of RE’s Transformation • Get “competent” bacteria (usually E.coli that is capable of being transformed) • Treat those cells to calcium chloride • Heat shock to force bacterial cell to take up plasmid DNA Now… • Select for bacteria that have taken up your plasmid (usually use antibiotic) • Grow bacteria in large quantities, purify out protein, and… PCR (polymerase chain reaction) • Specific sequence of DNA is amplified (copied many times) • Requires: – DNA template (contains your gene of interest) – Tac polymerase (a DNA polymerase that can work at high temperatures) – Nucleotides (to synthesize new DNA) – Primers (specific to the gene of interest) • PCR is a cyclic process: – Heat to denature (open up) DNA – Cool to allow primers to anneal (stick to) single stranded DNA – Warm to allow DNA to be replicated by polymerase – REPEAT Gel Electrophoresis • Uses a gel as a molecular sieve to separate pieces of DNA based on size • Smaller pieces travel further than larger pieces Let’s discuss some examples 1. Genetically modified food 2. Transgenic animals 3. Pharmaceuticals 1. Genetically Modified Food • Insert particular genes within a type of food to make it better tasting, longer lasting, or more healthy. • Long term effects of consumption of this food are unknown. 2. Transgenic Animals • Research purposes – Knock outs – Overexpression – Use of GFP to select for animals that are transgenic • Consumer purposes (food or medication) 3. Pharmaceuticals • Use plants or other GMO to produce pharmaceuticals – Ex: Gaucher’s disease (lysosomal storage disease – buildup of fat in cells); Pfizer received patent to grow drug to treat this disease in tobacco plant – Ex: Use of a transgenic goat to produce an anticoagulant (in the goat milk) to reduce probability of blood clots • Use bacteria to produce insulin, human growth hormone, clotting factors for hemophaelics • GMO mammals (mice) used in pharmaceutical research labs to study disease and treatment Your Homework: • Read the entire laboratory handout. You must carefully read the background information AND the laboratory procedure as well. • Answer the pre-lab questions.