* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
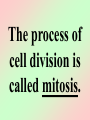
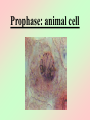
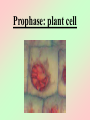
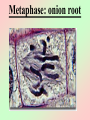
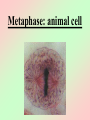
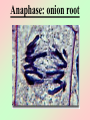
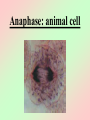
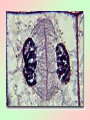
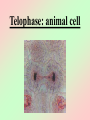
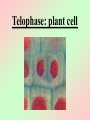
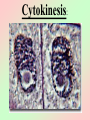
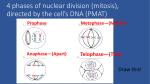
Cell Division We all start out as a single cell. That single cell has: •Cell membrane •Cytoplasm and organelles That single cell has: •Nucleus and a nuclear membrane That single cell has: •Chromatin (chromosomes) That single cell has: •Centrioles (only in animal cells) How do we become our multi-cellular selves? That first single cell must divide! One becomes two. Two cells become four. Four becomes eight. Eight becomes 16. 16 becomes 32. And so on. The process of cell division is called mitosis. It happens in 6 phases. Phase 1 Interphase Interphase: onion root Interphase: animal cell Interphase: plant cell •Cell is performing its usual life functions, and is not dividing •Chromosomes are thin and threadlike (called chromatin at this stage) •Near the end of phase one, the chromosomes are duplicated •The chromosome count doubles •The original and copy chromosomes are attached at an area called the centromere Phase 2 Prophase Prophase: onion root Prophase: animal cell Prophase: plant cell •The chromosomes shorten and become rod-like. This makes them stronger. •The centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell •A mesh-like bridge forms between the two centrioles •In plants, the bridge forms without centrioles •The nuclear membrane breaks down Phase 3 Metaphase Metaphase: onion root Metaphase: animal cell Metaphase: plant cell •The centromeres attach the chromosomes to the mesh-like bridge Phase 4 Anaphase Anaphase: onion root Anaphase: animal cell Anaphase: plant cell •The centromere splits, allowing the chromosomes to separate from their copies •The chromosomes and the copies move away from each other on the meshlike bridge, toward the centrioles Phase 5 Telophase Telophase: onion root Telophase: animal cell Telophase: plant cell •The chromosomes uncoil and become threadlike chromatin again •A nuclear membrane forms around the chromatin at each end of the cell Phase 6 Cytokinesis Cytokinesis: •The cell membrane pinches off equal amounts of cytoplasm •Each part contains a new nucleus, and there are two new cells! The end of Cell Division!