* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Semester Exam Review - Part One
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
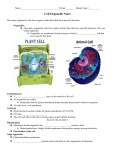
Name: ___________________ Date: ____________________ Hour: ____________________ BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAM REVIEW PART ONE CELL REVIEW 1) In the Venn Diagram below, compare and contrast a Prokaryote to a Eukaryote. (Make sure you include examples of each in your Venn Diagram.) PROKARYOTES SAME EUKARYOTES No Nucleus Smaller Bacteria Cell Type Has a Cell Membrane Has DNA Has a nucleus Larger Animals, Plants, Humans, Fungi 2) In the Venn Diagram below, compare and contrast a Plant Cell to an Animal Cell. PLANT SAME ANIMAL Cell Wall Chloroplast Block Shaped (Rectangular) Large Vacuole Cell Types DNA Nucleus Cell Membrane No Cell Wall No Chloroplast ”Blob” Like Many small vacuoles 3) The cell organelles are listed in the left column. The descriptions of the organelles are in the right column. The organelles are not matched with their description. In the third column, write the correct cell organelle letter and named next to the organelle description. CELL ORGANELLES ORGANELLE DESCRIPTION CORRECT ORGANELLE MATCH A PLASMA MEMBRANE Aids in movement of the cell; short, hairlike projections CILIA B CYTOPLASM Aids in the movement of the cell; long, moves with a whiplike motion FLAGELLA C CYTOSKELETON Captures light energy and CHLORPLAST converts it into chemical energy through a process known as photosynthesis; only in plant cells D NUCLEUS Digests wornout or extra LYSOSOMES organelles and food particles E RIBOSOME Directs all cell processes; contains cell’s DNA F ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Flexible, selectively CELL MEMBRANE permeable boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell G GOLGI APPARATUS Generates the energy for the cell; converts fuel particles into usable energy H VACUOLE Made of microtubules; aids in CENTRIOLES cell division I LYSOSOME Manufactures proteins; made of RNA & protein RIBOSOMES J CENTRIOLES Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into sacs called vesicles GOLGI APPARATUS K MITOCHONDRIA Responsible for production of ENDOPLASMIC proteins & lipids; transports RETICULUM materials L CHLOROPLAST Sac used to store food, VACUOLE enzymes, and other materials within the cytoplasm M CILIA Semifluid materials that organelles float in CYTOPLASM N FLAGELLA Supporting network of long thin protein fibers that form a framework for the cell; provides an anchor for the organelles inside of the cell CYTOSKELETON NUCLEUS MITOCHONDRIA CELLULAR TRANSPORT REVIEW 4) Define the following terms: a)DIFFUSION: THE MOVEMENT MOLECULES THROUGH A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE FROM AN AREA OF HIGH TO AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION b) OSMOSIS: THE DIFFUSION OF WATER THROUGH A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE; MOVES FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION c) ACTIVE TRANSPORT: MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES FROM AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION TO AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION; REQUIRES ENERGY d) PASSIVE TRANSPORT: MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION; DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY 5) Draw a picture of the cell membrane in the box below and label the following parts: Phospholipid Bilayer, Carbohydrate Chain, Protein Channel 6) Cellular transport and movement of molecules will occur until EQUILIBRIUM is reached. (An equal concentration of molecules inside and outside of the cell) CELLULAR REPRODUCTION/DIVISION REVIEW 7) What are the four stages of MITOSIS in order? PROPHASEMETAPHASEANAPHASETELOPHASE 8) Describe the main activities that occur in each phase of the cell cycle. Use the chart below to record your answers. CELL CYCLE PHASE DESCRIPTION INTERPHASE The cell grows and replicates its DNA and centrioles PROPHASE THE CHROMATIN CONDENSES INTO CHROMOSOMES; THE CENTRIOLES SEPARATE, AND A SPINDLES BEGINS TO FORM; THE NUCLEAR ENVELOPE BREAKS DOWNS METAPHASE THE CHROMOSOMES LINE UP ACROSS THE CENTER OF THE CELL; EACH CHROMOSOME IS CONNECTED TO A SPINDLE FIBER AT ITS CENTROMERE ANAPHASE THE SISTER CHROMATIDS SEPARATE INTO INDIVIDUAL CHROMOSOMES AND ARE MOVED APART TELOPHASE THE CHROMOSOMES GATHER AT OPPOSITE ENDS OF THE CELL AND LOSE THE DISTINCT SHAPES; TWO NEW NUCLEAR ENVELOPES WILL FORM CYTOKINESIS THE CYTOPLASM PINCHES IN HALF; EACH DAUGHTER CELL HAS AN IDENTICAL SET OF DUPLICATE CHROMOSOMES 9) What is the result of one phase of mitosis? (How many cells? How many chromosomes do the cells have? Are they identical to each other?) TWO IDENTICAL CELLS WITH 46 CHROMOSOMES