* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NOTES Organelle Structure and Function
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
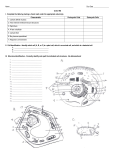
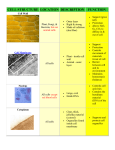
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell ◦ Most are surrounded by a membrane ◦ Each helps to maintain life of the cell Parts of the Cell Cell Membrane Model Phospholipids and proteins move laterally ( side to side) for short distances. Proteins make a pattern on the surface known as the fluid mosaic model. CELL MEMBRANE or PLASMA MEMBRANE Mainly made of phospholipids and proteins. HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer (double layer). ◦ POLAR head facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in. Membranes are selectively permeable - they allow certain molecules to pass through, but keep others out. ◦ In plants and bacteria, this is within the cell wall. Cytoplasm is the “gel-like material and organelles” between the nucleus and cell membrane. NUCLEUS and NUCLEOLUS NUCLEUS IS: •Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane (nuclear envelope). • Nuclear pores allow molecules in and out. •Serves as the COMMAND CENTER OF CELL; directs cell’s activities. •CONTAINS CELL’S GENETIC MATERIAL (DNA). •Contains NUCLEOLUS (dark spot) which makes RIBOSOMES which makes proteins. DNA is scrunched up as chromosomes in DIVIDING CELLS. DNA is spread out as chromatin in NONDIVIDING CELLS. CYTOSKELETON Cell’s skeleton. Made of PROTEINS called microtubules and microfilaments. FUNCTION: Give the cell shape, strength and the ability to move. Lysosome Sac containing digestive enzymes. FUNCTION: Digests: food particles, disease-causing bacteria and viruses, and worn out or broken cell parts. ◦ Plays a role in apotosis “programmed cell death”. Cell suicide for the good of the organism. Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal. VACUOLE Animal: ◦ Sac for storage, digestion, and waste removal. ◦ Contains water solution. Plant: ◦ Large, central vacuole; stores water and nutrients needed by cell. ◦ Help support the shape of the cell. Huge in plant cells, small in animal cells, NOT in prokaryotic cells. CENTRIOLES Made of PROTEINS called microtubules. Found only in animal cells. FUNCTION: aid in movement of chromosomes during cell division. CILIA and FLAGELLA Made of PROTEINS called microtubules organized in a nine/two arrangement that help with movement. FUNCTION: external appendages from the cell membrane that aid in locomotion (movement) of the cell. RIBOSOMES Can be free in the cytosol or bound to the surface of Rough ER. MADE OF proteins and RNA FUNCTION: make protein for use in the cell (free) or for export (bound). MITOCHONDRION (plural: MITOCHONDRIA) Surround by double membrane. Contains its own DNA. Called the powerhouse of cell. Site of cellular respiration (use glucose to produce cell energy, ATP). Permeable outer membrane. Folded inner membrane = cristae (increases surface area for more chemical reactions). GOLGI APPARATUS (BODY) Looks like a stack of flattended sacs. FUNCITON: Modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids made by ER for transport out of cell. Enclose digestive enzymes into membranes to form lysosomes. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) ROUGH ER/SMOOTH ER Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface, while smooth does not; continuous with nuclear envelope. FUNCION ROUGH ER: Internal delivery system of the cell; makes, processes, and transports proteins to be exported outside the cell. FUNCTION SMOOTH ER (no ribosomes): produce lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. CHLOROPLASTS Where photosynthesis takes place (produces plant food (sugars) and oxygen gas. Contains green pigment, chlorophyll. Flattened membrane sacs called thylakoids contain CHLOROPHYLL ; stacks of thylakoids called grana. Gel like material around thylakoids called stroma. FOUND ONLY IN plant CELLS. CELL WALL Found OUTSIDE the cell membrane in plant cells and bacteria only. Contains cellulose that provides support (rigidity) and protection. Bacteria have cell walls made of sugar and proteins instead of cellulose. PROKARYOTES Bacteria are the most common prokaryotic cell. They do not have a nucleus, but do contain a single loop made of DNA. Like all cells, bacteria are surrounded by a cell membrane which contains the gel-like cytoplasm of the cell.