* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane Notes
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
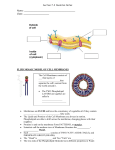
Cell Membrane Notes Cell ___________________ are composed of 2 ___________________ layers. (bilayer) The Outer “heads” of the phospholipid really like water and are called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ________________. Draw and label one phospholipid in the box to the right: The ___________________ membrane has 2 major ___________________: 1. forms a ___________________ between inside and ___________________ of the cell 2. controls ___________________ of ___________________ The fluid ___________________ model ___________________ the membrane-how? Explain: There are other ___________________ embedded in the ___________________. Label the compounds in the membrane below: Macromolecule compounds Protein Function Membrane proteins: Channel proteins: Membrane receptor proteins: Intracellular receptor proteins: Carbohydrate Lipids/Fats (________) Do ______mix with water. Cholesterol: Phospholipid bilayer: Use figure 3.18 to draw an example of selectively permeable or semipermeable membrane in the box to the left and fill in the blanks: The cell membrane is ___________________ permeable. Allows ____________, but not ____, _________________to cross Go to http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter17/animation__i ntracellular_receptor_model.html After you watch the animation, explain how cell signaling works using the terms ligand and receptor protein: 1) Why do phospholipids form a bilayer in the cell membrane? 2) How does a sieve (or a colander) demonstrate selective permeability? 3) Based on your knowledge that membranes are also found around all organelles, how do you think organelles came to be part of the cell?