* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelle stations
Survey
Document related concepts
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
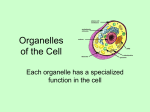
Organelle Learning Sta-ons The purpose of this ac-vity is for you to explore and increase your knowledge about cell organelles. Notes have been provided. Please add diagrams and take the -me to learn about each organelle Structure Composed of a bi-‐layer of phospholipids with proteins embedded in it Func*on • holds cell together and gives shape • regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell Nuclear membrane Nuclear pore Nucleolus Chromatin Nucleoplasm Structure: • Dark granule in center of cell • Surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope/membrane Func-ons: – Controls cell ac-vi-es through protein synthesis – Contains gene-c info – Directs cell division – Site of DNA replica-on and transcrip-on Structure • small, dark spot in nucleus • Made up of RNA • No membrane Function • makes rRNA, which then make ribosomes Structure: • a double membrane made of phospholipids which has nuclear pores Function: – Separates nuclear material from cytoplasm – Pores allow RNA and proteins in & out of nucleus This is DNA (found in the nucleus). During a cell’s life cycle, the DNA mostly exists in this form. 1. Chromatin is densely coiled DNA wrapped around histone proteins. 2. Only condenses into chromosomes before cell division (mitosis or meiosis). Structure • double membrane of phospholipids • inner membrane is very folded =CRISTAE (increased surface area for cellular respira-on) • fluid in between = MATRIX • has its own DNA Func*on: “powerhouse” – makes ENERGY (ATP) for the cell in a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Converts chemical energy in food to ATP Structure • membrane channels running from the nuclear envelope throughout cytoplasm. It is a transport system. 2 Types: • Means has ribosomes attached • Usually connected with the nuclear membrane. • Ribosomes make proteins and then place them in the rER • The rER packages proteins in a vesicle and sends them to the Golgi Body. • Has no attached ribosomes. • Makes lipids and steroids. • Also detoxifies harmful material or waste products • You’ll find a lot of sER in liver cells and glands that make hormones. Structure • small, dense granules made of rRNA & protein • No membrane • 2 subunits (large & small) Function • site of protein synthesis (translation) • Usually attached to rER so proteins can be easily exported • Can be free in cytoplasm -proteins not exported (aka Polyribosome) Structure • Free floa-ng group of ribosomes Func*on • makes large proteins (faster) with a single mRNA molecule (or golgi apparatus or golgi complex) Structure • stacks of flaYened sacs • surrounded by vesicles Func*on • Collects, sorts, packages and distributes materials in the form of vesicles • modifies proteins and lipids from ER 1. DNA copies a gene as mRNA 2. mRNA moves through pore and attaches to ribosome to make protein 3. Protein put into rER, then sent to Golgi in a transport vesicle 4. Golgi modifies protein, repackages and sends it to plasma membrane in a secretory vesicle. 5. Protein released at the plasma membrane via exocytosis Use a laptop or computer to view the animation of how these organelles work together to release protein … turn narration on (need flash) http://bcs.whfreeman.com/ thelifewire8e/content/ cat_040/0404002.html And http://life9e.sinauer.com/ life9e/pages/ 05/052001.html - To go over how glycolipids are formed - Add to notes if needed. Structure • Small, membranous (bilayer) bound sac usually made by Golgi body Func*on • Storage sac (temporary storage) ex. H2O, food, digestive enzymes, hormones. 2 types: Transport vesicle: moves substances from ER to Golgi Secretory vesicle: moves substances from Golgi to cell membrane Structure Func*on • large vesicle (but small in • Long term storage of H2O animals) and typically one with dissolved sugars and large in plants salts • Membranous sacs Vacuoles are larger Plant cell Vacuole and are formed by phagocytosis (cell eating). Structure • Double membraned vacuoles with hydroly*c (diges-ve) enzymes Func*on • Hydrolysis! Breaks down… • destroys harmful substances • can kill the cell if it breaks open -‐ “suicide sacs” • many in white blood cells Watch the animation about lysosomes on youtube http:// www.youtube.com/ watch?v=ekdIEpSf-1I Go to youtube.com, search “McGraw Hill lysosomes” and watch the first video. series of protein fibres in the cytoplasm • Maintains cell shape • Monorail to transport organelles around the cell • Assemble and disassemble as needed Made up of: • • • • aka ac-n filaments Long & thin protein fibres that give structure and support to membrane Anchored to the plasma membrane Organelles move around the cytoplasm on these Example: in muscle cells Ac0n interacts with motor molecules such as myosin. • In the presence of ATP, myosin pulls ac@n along causing contrac@on Structure • Largest fibre • Cylinder shaped & made of tubulin (protein) Microtubule Func*on • Anchor for organelles and monorail for organelle movement • Used to make cilia, flagellum & centrioles Structure • Intermediate size between ac-n filaments and microtubules • made of kera-n Func*on • Keeps the nucleus in place • Cell-‐cell junc@ons, such as those holding skin cells @ghtly together Structure • ‘Watery gel’ between cell membrane and nuclear envelope • Contains water with dissolved salts, proteins & other organic compounds Func*on • Support & suspend organelles • Provide water • allows diffusion to occur in cells Structure • Double membrane of phospholipids • inside stacks of discs called GRANUM • contain: – their own DNA – ribosomes – enzymes Func*on • photosynthesis (light energy converted into chemical energy) ATP + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Granum= contains chlorophyll which traps solar energy Structure • Tough, rigid outermost wall • made up of cellulose (very strong) Func*on • maintains cell shape and skeletal support Label & explain the inter-‐rela-onships between cell organelles Explore the organelles within a cell http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/ insideacell/ (does not work on iPads) Plug in your earbuds to the laptop/computer and explore the organelles. Find and listen to: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoskeleton 3. Lysosomes 4. Golgi apparatus 5. Mitochondria 6. Endoplasmic reticulum Review of Organelles….Test yourself. This learning app provides you a narrated overview (plug in your earbuds) of the organelles and finishes with an activity that allows you to test your knowledge. Give it a try on a laptop or computer (not an iPad) http://www.wisc-online.com/Objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11403 Can you identify the parts of an animal cell? Test yourself. http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/U1animalcells.htm How about a plant cell? Test yourself. http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/U1plantcells.htm Can you determine the functions of the organelles? Test yourself. http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/U1Organelles.htm iPad or desktop: Beautiful 3D animation of the inside of the cell Watch the video and try to identify as many parts of the cell as possible. Youtube.com search “Inner life of a cell” & watch the 3:13 one http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wJyUtbn0O5Y This is quite a realistic representation.