* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
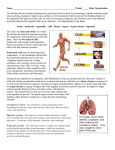
The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System Introduction • Nervous System –Central Nervous System (CNS) –Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Nerves The Peripheral Nervous System • Somatic Nervous System • Autonomic Nervous System –Sympathetic nervous system –Parasympathetic nervous system Types of Neurons: • Sensory Neurons: Collect messages from sense organs & carry those messages to the spinal cord or brain. • Motor Neurons: Carry messages from the spinal cord or brain to muscles and glands • Interneurons: Carry messages from one neuron to another A Simple Reflex A Simple Reflex A Simple Reflex The Endocrine System: the body’s “slow” chemical communication system: a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Glands we need to know: Pituitary Thyroid/Parathyroid Adrenal Gonads (Sex Glands) Glands: Units of the body that secrete hormones. The Endocrine System The Glands The Pituitary Gland: The Master Gland; It activates other glands and controls the growth hormone. Hormones: Chemical regulators that control bodily processes in the bloodstream such as emotional responses, growth, and sexuality. The Endocrine System The Glands The Thyroid Gland: The gland that controls and regulates the speed of bodily processes called metabolism. Metabolism: The speed at which the body operates or the speed at which it uses up energy. Parathyroid GlandsRegulates the calcium levels in the blood The Endocrine System The Glands The Adrenal Glands: Glands that cause excitement in order to prepare the body for an emergency or for some important activity. Adrenaline (Epinephrine): Chemical that prepares the body for emergency activity by increasing blood pressure, breathing rate, and energy level. The Endocrine System The Glands The Gonads: The sex glands; They make sperm or eggs for reproduction. Testosterone: The male sex hormone. Estrogen: The female sex hormone. Nervous System = the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Central Nervous System = the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System = the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body. Nerves = bundled axons that form neural “cables” connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs. Somatic Nervous System = the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles. It allows for the voluntary control of our muscles. • Also called the skeletal nervous system. • Walking, running, and jumping- You are using your somatic nervous system. Autonomic Nervous System = the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). • Controlling involuntary muscles. “Those that are on autopilot” Sympathetic Nervous System = the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System = the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.