* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
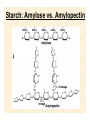
Download Starch: Amylose vs. Amylopectin
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
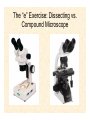
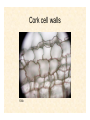
Starch: Amylose vs. Amylopectin Lab Manual 1.Microscopes and Plant Cells Lab 1.25.12 Pre-Lab Quiz 1. Say your oculars have a 10x magnification. If you are looking at a specimen using the 40x objective, what is your total magnification? 2. What is the name of the moveable structure to which the objectives are attached? 3. What do the leucoplasts found in potatoes store? 4. What is the special name for these storage structures? 5. How do some plants cope with the build up of toxic substances? The Compound Microscope • Always carry microscopes with 2 hands: one at the base, one at the arm • Demo of microscope parts • Always make sure you’re on the lowest objective when mounting or removing slides • Wipe up spills immediately so you don’t destroy the lenses Outline for today’s lab: • The letter E • Cork cells- cell wall • Onion- cell wall, nucleus, nucleoli, cytoplasm, vacuoles... Add IKI if necessary • Elodea leaf- cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuole (tonoplast)... Add NaCl if you want to see plasmolysis. • Potato tuber- leucoplasts (amyloplasts), intercellular spaces • Red pepper- chromoplasts • Zebrina- raphides • Begonia- druses The “e” Exercise: Dissecting vs. Compound Microscope “Depth of Field” How thick of a slice can I get in focus at once? y y z z x Lower magnification x Higher magnification Representative Plant Cell Cork cell walls 100x Onion and IKI IKI (Lugol’s solution) should turn black in the presence of starches. It should help you distinguish between some of the different cellular compartments. Elodea and Plasmolysis Waterweed (Elodea densa) a submersed South American aquarium plant that is naturalized in ponds, streams and lakes throughout North America. The cartoon cell to the left shows a living photosynthetic cell. Because most of the cell is occupied by a water-filled, large central vacuole, the chloroplasts are displaced around the periphery of the cell, just inside the cell wall and membrane. The cell on the right has shrunken away from the cell wall (plasmolysis) due to water loss caused by disruption of its osmotic balance. Potato tuber Red Pepper Different Plastids in Plants Precursor of all plastids Chloroplasts not yet exposed to light Site of photosynthesis Monoterpene synthesis; precursor to other plastids Synthesize and store pigments Starch storage Fat storage Protein-modifying compounds Zebrina Raphides Begonia Begonia Druses Begin lab exercises!