* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BioCore II lecture6
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
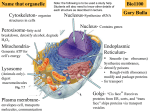
1. Sit with Lab Group Find members of your group 2. Attendance with your phone Launch your Top Hat app on your smart phone or load the TopHat.com website, or text to the course’s phone number. Prepare for Pop Quiz at start of lecture Pop Quiz! 2 If you were a prokaryotic cell, you would be lacking _____. a. a plasma membrane composed of phospholipids and proteins b. chromosomes that contain genetic information c. ribosomes to synthesize proteins d. mitochondria to generate ATP Why is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum unable to synthesize proteins? a. b. c. d. It has no ribosomes. There is no supply of free amino acids that it can easily access. It stores calcium, which is known to inhibit protein synthesis. It has no DNA to direct the synthesis of proteins. What does a motor protein do in a cell? a. b. c. d. causes microtubules to “treadmill” converts ATP into mechanical energy in the form of movement triggers receptor-mediated endocytosis aids in the transport of newly synthesized proteins from the endomembrane system e. Some of the above f. All of the above Which of the following is NOT considered a benefit of compartmentalization in eukaryotes? a. Chemical reactions are more efficient because substrates are more easily maintained at high concentrations within organelles. b. Chemical reactions that are incompatible can be segregated in different organelles. c. DNA is transcribed and translated at significantly higher rates because all of the machinery is inside a single, membrane-bound nucleus. d. When the product of one reaction is the substrate for a second reaction, the enzymes that work together can be clustered together on internal membranes and result in greater speed and efficiency. Molecular “zip codes” direct molecules to specific destinations in the cell. How do you predict these signals are read? a. They bind to receptor proteins. b. They enter transport vesicles. c. They bind to motor proteins. d. They are glycosylated by enzymes in the Golgi apparatus. END Pop Quiz! 8 ANY Questions about Pop Quiz? 9 Glucose Pancreas secretes INSULIN Glycogen Insulin causes cells in the liver and skeletal muscle to synthesize glycogen; fat storage cells synthesize triglycerides. Glucose levels fall HOMEOSTASIS If glucose levels too low Pancreas secretes GLUCAGON (normal glucose levels in blood) Glucose levels rise Glucagon causes cells in liver and skeletal muscle to catabolize glycogen; fat storage cells catabolize fatty acids. Glycogen Glucose Last time…Chalk Talk “How to make the hormone insulin” NOW: Must learn biosynthesis path for -> nuclear, membrane, cytoplasmic Review the drawing: what is the mutant path? What happens at the end for insulin, a secreted protein? Sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins takes place in the Golgi apparatus, which are? Send me photos of your art for bonus points Which structure is not part of the endomembrane system? Which structure is not part of the endomembrane system? A. B. C. D. E. nuclear envelope chloroplast Golgi apparatus plasma membrane ER What correctly characterizes “bound” ribosomes? If you inject lots of radioactively labeled S-35 leucine (it’s an amino acid) into a pancreatic cell making hormones.… what is the likely path the radioactivity will take?