* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Q: True or False? Cells do everything needed for life. Q: What are all
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
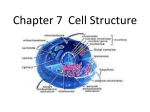
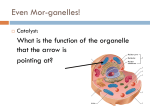
Q: True or False? Cells do everything needed for life. A: True. The cell is the basic unit of all life. Q: What are all organisms made of? A: cells Q: Where do all cells come from? A: other cells Q: What keeps the size of most cells very small? A: the surface area-t0-volume ratio Q: What protects the inside of a cell from the outside world? A: the cell membrane Q: How are archaebacteria different from eubacteria? A: Archaebacteria have different ribosomes. Q: What is the fluid inside a cell called? A: cytoplasm Q: What packages and distributes proteins for a cell? A: the Golgi complex Q: What is the job of the lysosomes? A: they digest food particles Q: What is the genetic material in a cell called? A: DNA Q: Where is DNA found in eukaryotic cells? A: it is found in the nucleus Q: What do you call cells that have a nucleus? A: eukaryotic Q: What do you call cells that do not have a nucleus? A: prokaryotic Q: What are the stiff surfaces that support plant and fungi cells? A: cell walls Q: What is the organelle that makes proteins? A: ribosomes Q: What is the cell’s delivery system called? A: endoplasmic reticulum Q: What is the lowest level of organization in an organism? A: the cell Q: What forms a tissue? A: cells that are like each other and do the same job Q: What is the definition of an organ? A: a structure made of two or more tissues working together Q: What do you call a group of organs that work together? A: an organ system Q: Larger size, longer life, and more-specialized cells are all characteristics of what kind of organisms? A: multicellular Q: What else did Hooke and Leeuwenhoek do either than help discover cells? Q: they helped develop the microscope Q: What is another name for the “animalcules” that Leeuwenhoek found in pond scum? A: protists Q: True or False? “All plant parts are made of cells. A: True. This is the information that Schleiden added to the cell theory. Q: Name the three parts of the cell theory. A: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. Q: Why are most cells very small? A: Their volume is limited by how large their surface area is. Q: What is the part of the cell that keeps the cytoplasm inside and controls materials going in and out of the cell called? A: cell membrane Q: What are the structures that are usually surrounded by membranes and which perform specific functions within the cell called? A: organelles Q: what is an organelle that contains the cell’s deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) called? A: nucleus Q: What is a single-celled organism that has no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles called? A: prokaryote Q: What is the smallest and most common form or prokaryotes, containing DNA, ribosomes, and a flagellum called? A: eubacteria Q: What group of prokaryotes include such types as heat-loving, salt-loving, and methane-making? A: archaebacteria Q: What are organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles called? A: eukaryotes Q: What word describes most organisms that you can see with your naked eye? A: multicellular Q: What do you call an organism with only one cell? A: unicellular Q: What are the cell walls of plants made of? A: cellulose Q: What are the cell walls of fungi made of? A: chitin or a chitin-like material Q: Do animal cells have cell walls? A: No Q: Do plant cells have cell walls? A: Yes Q: Do fungi cells have cell walls? A: Yes Q: What part of the cell forms a barrier between the cell and its environment? A: cell membrane Q: What does the cytoskeleton do? A: One of its functions is to keep the cell membrane from collapsing. Q: The nucleus has DNA. What does the DNA carry? A: The DNA carries the genetic material with instructions for how to make proteins. Q: What do ribosomes do? A: They make proteins. Q: Where are ribosomes found? A: on the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum Q: What organelle of the cell acts as the cell’s delivery system? A: the endoplasmic reticulum Q: What process adds oxygen to food and releases energy? A: cellular respiration Q: What do you call the energy released from cellular respiration? A: ATP Q: Where does cellular respiration happen in the cell? A: mitochondria Q: What cell parts carry materials between organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex? A: vesicles Q: What are three advantages of multicellular organisms? A: larger size, longer life, and specialization Q: What is the function of a part of an organism is related to? A: the structure of that part Q: Put the following in order according to its complexity. Organs, tissues, organ systems, cells, organisms A: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms (Note that each level of organization is more complex that the level below it.) Q: What do you call the study of cells? A: cytology