* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Bio Study Guide
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
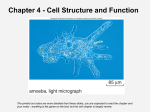
Name: ____________________________________ Date: ________________ Block: ___________ Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function Study Guide 1. List the three parts of the cell theory. 1. 2. 3. 2. List the unique features of a prokaryotic cell: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. List the unique features of a eukaryotic cell: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 4. What limits a cell’s size? Explain. 5. Where is DNA located in a prokaryote? ________________________________________________ 6. Where is the genetic material for the cell located? ________________________________________ 7. What are the specific structures in eukaryotic cells called? __________________________________ 8. Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? _____________________________________________ 9. What is the difference between smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum? 10. Where are proteins made in the cell? ___________________________________ 11. Which organelle moves proteins through the cell? _________________________________ 12. Which organelle sorts, modifies, and packages proteins? ____________________________ Name: ____________________________________ Date: ________________ Block: ___________ 13. Where is energy stored and created in the cell? ____________________________________ 14. Which organelles help a plant during photosynthesis? _______________________________ 15. Which organelle is most responsible for maintaining homeostasis? __________________________ 16. Describe colonial organisms. 17. What are the 3 structures present in a plant cell but not in an animal cell? 1. 2. 3. 18. Which scientist named the cell? ___________________________________ 19. Which scientist discovered that all plants had cells? ________________________________ 20. Which scientist discovered that all animal cells have cells? __________________________ 21. Which scientist discovered that all cells arise from existing cells? ___________________________ 22. How are chloroplasts and mitochondria similar? Different? 23. Put the following terms in order from smallest to largest: organ, cell, organ system, tissue. Refer to the illustration below. 24. Label and give the function of 1 – 5 in the diagram below and state whether the cell shown is a plant cell, animal cell, or prokaryotic cell. Name: ____________________________________ Date: ________________ Block: ___________ 25 – 41. On a separate sheet of paper, define the following: cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosome, prokaryote, eukaryote, nucleus, vesicle, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondrion, flagellum, tissue, organ, organ system. For each of the words below, circle whether they are located in prokaryotes, plants, or animals. 42. cell membrane: prokaryote plant animal 43. cytoplasm: prokaryote plant animal 44. ribosome: prokaryote plant animal 45. nucleus: prokaryote plant animal 46. vesicle: prokaryote plant animal 47. endoplasmic reticulum: prokaryote plant animal 48. Golgi apparatus: prokaryote plant animal 49. central vacuole: prokaryote plant animal 50. chloroplast: prokaryote plant animal 51. mitochondrion: prokaryote plant animal 52. flagellum: prokaryote plant animal 53. cell wall: prokaryote plant animal Label the following diagram, including the polar head and non-polar tail. 55. What part of the cell does this lipid bilayer form? _____________________________________ 56. Why is the phospholipid bilayer important to the cell? 57. Does passive or active transport require energy? ______________________________________ 58. Is diffusion passive or active transport? ____________________ Osmosis? ________________ Name: ____________________________________ Date: ________________ 59. What happens when a solution is hypertonic? Block: ___________ 60. What happens when a solution is hypotonic? 61. What happens when a solution is isotonic? 62. Do the cells in our bodies prefer to be hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? __________________ 63. Label the following diagrams with the terms exocytosis and endocytosis. 64. How is a particle able to move from a region of lesser concentration to a region of higher concentration? 65. Define diffusion. 66. How do large molecules cross the cell membrane? 67. Ions moving through ion channels move due to what type of transport? ____________________ 68. If you pour ink into a beaker, what term is used to describe the dispersal of the ink?