* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Steps for completing this study guide I Have, Who Has Matching
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
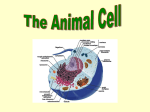
Name:____________________________________ Block:________ Steps for completing this study guide 1. When you come to a station, attempt to answer each question for that station. 2. Once you are done answering the questions, or if you can’t answer the question, play the game. 3. Follow the directions of each game. Record your time or tally when appropriate. 4. Once you have completed each game you will be able to answer the question. 5. You will have about 10 minutes at each station. I Have, Who Has 1. We know that Structure Function determines the effect of how something is made, or shaped, affects what it is able to do. (For example, the Cell Wall is made of thick fibers so it can protect the cell.) Write down one more example of Structure Function within the cell. Record your time. Round 1:_____________ Round 3:_____________ Round 2:_____________ Round 4:_____________ Cytoplasm is fluid enough so that materials can move throughout the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum is long and tubular so that it can transport proteins. 2. Give an example of Division of Labor within a cell. The ribosomes help produce a protein and the endoplasmic reticulum helps move that protein throughout the cell. Matching Puzzle 3. Name an example of a single celled organism. Record your time. Round 1:_____________ Round 3:_____________ Round 2:_____________ Round 4:_____________ E coli, Amoeba, paramecium, or many more 4. Why are ribosomes important to ALL cells? (Plants, animals, bacteria) Ribosomes make the proteins. Proteins are necessary to help all cells carry out different functions. 5. Why do all cells have cell membranes? All cells need cell membranes as a boundary. Plant cells and animal cells also need them to help contain all of the organelles that are found within a cell. Smart Board Activity Label the organelle parts in pencil. Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Nucleus Cytoplasm Chloroplast Vacuole Mitochondria Cell Wall Cell Membrane Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Cytoplasm Vacuole Mitochondria Cell Membrane Match organelle with definition on the second slide of the Smart Board. 5. What organelle is missing? What is its function? Ribosome. The Ribosome helps create proteins. Label the Plant Cell on the Smart Board, then check your answers. How Many did you get correct? 1st try__________________________ 2nd try_________________________ Label the Animal Cell on the Smart Board, then check your answers. How Many did you get correct? 1st try__________________________ 2nd try_________________________ Draw Something 6. Draw the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell. Place a tally in this box every time you correctly guess someone’s drawing. 7. What is the job of the endoplasmic reticulum? The Endoplasmic Reticulum is responsible for transporting proteins within the cell. 8. What organelle is found near the E.R.? Why are they close to one another? Ribosomes. They both work with proteins in the cell. 9. Draw a plant cell and an animal cell with a cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuoles, nucleus, and cell wall (if necessary). Label the vacuoles in both the plant and animal cells. One Large Vacuole Small Vacuoles 10. What is the job of the vacuole? The vacuole is responsible for storing water and other nutrients within the cell. Taboo Place a tally in this box every time you correctly guess someone’s drawing. 11. Draw a Chloroplast. 12. Why are plant cells the only type of cell that has chloroplasts? Chloroplasts are where photosynthesis occurs. Since Animals and bacteria do not use photosynthesis, plants are the only type of cell that needs chloroplasts. 13. Draw a Mitochondria. 14. Why do both plants and animals have mitochondria? Mitochondria are responsible for converting materials and producing ATP, or cellular energy. Both plant cells and animal cells convert glucose (stored energy) into ATP in their mitochondria. 15. What does it mean to be unicellular? Made of only 1 cell. 16. How many cells must an organism have to be considered living? Only 1. Head's Up Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Cell Wall Many Small Vacuoles Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Mitochondria Chloroplasts One Large Vacuole Place a tally in this box every time you correctly guess someone’s drawing. 17. Place each of the 9 organelles inthe Venn Diagram to show where they are found in plant and animal cells. Plants Animals Both Cell Wall Many Small Vacuoles Nucleus One Large Vacuole Ribosomes Cytoplasm Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Mitochondria 18. Draw a Nucleus 19. What is the function of the nucleus? The nucleus stores the DNA and is responsible for giving instructions to the cell and the other organelles. 20. Draw Ribosomes. 21. What is the function of the Ribosome? The Ribosome helps create proteins. Yahtzee 22.Explain the difference between mitochondria and chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are found in only plant cells, and are responsible for taking in sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose, or sugar for the cell. Mitochondria finish the process that takes that glucose and converts it into cellular energy known as ATP. 23. Explain the difference between Cell Membrane and Cell Wall. The Cell Wall is found only in plant cells. It is made of a hard, rigid material and it gives supports and protects the cell. The Cell Membrane is found in both animal and plant cells. The membrane contains all of the organelles and decided what is allowed to enter and exit the cell. 24. Draw the Cell Wall and Cell Membrane in a Plant Cell. Cell Membrane Cell Wall 25. What is the function of cytoplasm? Cytoplasm is a jelly like substance that suspends the organelles and allows certain things to travel throughout the cell.