* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structures and Function
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
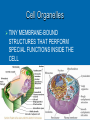
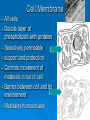
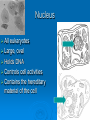
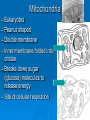
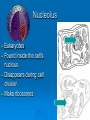
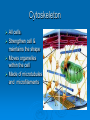
Agenda Standard Cell Organelle Notes Cell Organelle Campaign Standard SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. Cell Structures and Function Cell Organelles TINY MEMBRANE-BOUND STRUCTURES THAT PERFORM SPECIAL FUNCTIONS INSIDE THE CELL Cell Wall Plant, Fungi, & Bacteria, but not animal cells Outer layer Rigid & strong Made of cellulose Provide support and protection Cell Membrane All cells Double layer of phospholipids with proteins Selectively permeable support and protection Controls movement of materials in/out of cell Barrier between cell and its environment Maintains homeostasis Nucleus All eukaryotes Large, oval Holds DNA Controls cell activities Contains the hereditary material of the cell Cytoplasm All cells Clear, thick, jellylike material Contains the cytoskeleton fibers Supports and protects cell organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotes Network of tubes or membranes Smooth w/o ribosomes Rough with embedded ribosomes Carries materials through cell Aids in making proteins Ribosomes All cells Small bodies; can be free or attached to ER Made of rRNA & protein Synthesizes proteins Mitochondria Eukaryotes Peanut shaped Double membrane Inner membrane folded into cristae Breaks down sugar (glucose) molecules to release energy Site of cellular respiration Vacuole Plant (large), Animal (small) Fluid-filled sacs Largest organelle in plant cells Store food, water, metabolic & toxic wastes Store large amounts of food or sugars in plants Lysosomes Plant (uncommon), Animal (common) Small and round with a single membrane Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules Digests old cell parts Chloroplast Plant and Algae Green, oval containing chlorophyll (green pigment) Uses energy from sun to make food (glucose) Site of photosynthesis Release oxygen Nucleolus Eukaryotes Found inside the cell's nucleus Disappears during cell division Make ribosomes Golgi Apparatus (Body) Plant and Animal Stacks of flattened sacs Modify proteins made by the cells Package & export proteins and lipids Flagella and Cilia Some animal cells, prokaryotes Cilia are short and numerous Flagella are long, usually only one or two on a cell Provides movement for the cell Made of microtubules Centrioles Animal Made of microtubules and microfilaments Strengthen cell & maintains the shape Moves organelles within the cell Cytoskeleton All cells Strengthen cell & maintains the shape Moves organelles within the cell Made of microtubules and microfilaments