* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Period _____ The Cell Theory 1.
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
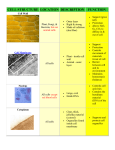
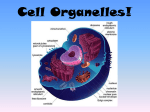
Name ____________________________________________________________ Period _____ The Cell Theory 1. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Cells are the basic units of _________________ and _________________ in organisms. 3. ________________________________________________________________________ Things all cells have in common: 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 4. ___________________________ 5. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ Cell Types Prokaryotes – _________________________ Eukaryotes – Unicellular (Protozoa) = ________________________ – ______________________ – ______________________ – ______________________ Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Peptidoglycan cell wall Cell Wall (Fungi, Plants) or Not (Animals) – Not made of peptidoglycans Plasma/Cell Membrane = “Gatekeeper” Lipid ____________________ Filters what goes in and out – Active Transport (Sodium) – Facilitated Transport (Glucose) – Passive Diffusion (Water) _______________________________________________________________ Cell Wall = “Retaining wall” Peptidoglycans in prokaryotes – Targeted by antibiotics like penicillin Also in fungi and plants – Different chemistry (_________________________ in plants) – Provides rigid _______________________ Nucleus = “Brain of the cell” Consists of: – __________________________________________ – ________________________ (DNA + proteins) – ________________________ (rRNA ribosomes) DNA replication and transcription occurs in the nucleus Controls all cell activities. Centrioles = “Construction Foremen” Found only in _____________________ cells (US!) Directs construction of the spindle during cell division Composed of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in a circle. Come in pairs Mitochondria = “Powerhouse of the Cell” __________ (energy) production occurs here All mitochondria come from ___________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Inner and Outer membrane space with cristae in between May have originally been a “captured” bacterium put to use by cell Ribosomes = “Factories of the Cell” Found free in cytoplasm or attached to ER __________________________ mRNA (from DNA) into protein Two subunits – 50S and 30S 70S in prokaryotes – 60S and 40S 80S in eukaryotes – Made up of proteins and rRNA Not a true organelle (found in prokaryotes) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) = “Highways of the Cell” ___________________ (with ribosomes) – Membrane protein synthesis – Transport and vesicle formation ___________________ (no ribosomes) – Synthesis and metabolism of lipids – Detoxification (lots in liver cells) Golgi Apparatus = “UPS for the Cell” ______________________________________________________________ – Processing of proteins to final form – Packaging into ____________________ – Distribution of vesicles to final destinations (secretion, membranes, etc.) Lysosomes and Peroxisomes = “Garbage Disposal of the Cell” Lysosomes – Highly __________________ – Have pH sensitive enzymes that break down proteins and lipids Peroxisomes – Produce and metabolize H2O2 – May impact aging? (get/leak more as you age) Vesicles = “Transport Bins of Cell” Bud off of and merge with membranes _________________________ – forms vesicle carrying substance into the cell _________________________ – vesicle carries (secretes) substance out of the cell Cytoskeleton = “Skeleton and motion of cell” Three basic types: – Microtubules – Actin filaments – Intermediate filaments _____________________________ serve as microtubule organizing center – In animals, the centrosome has two centrioles, which play role in cell division forming the _______________________________________ Cytosol (cytoplasm) =“Soup of the Cell” Made up of _________________, ions, and macromolecules of the cell Organelles float within cytosol Many _____________________ and signaling cascades take place within the cytosol Chloroplasts =“Solar Cells of Plants” _____________________________________________________ (Photosynthesis) Stacked grana and thylakoid membranes filled with chlorophyll (green pigment) Energy stored via the Calvin (Dark) Cycle using carbon dioxide to form sugar Vacuoles = “Water Tower in Plants” __________________________________________; used for storage One large central vacuole in plants Membrane surrounds water or other storage materials Also supplies “_____________________________________” against cell wall of plants to allow them to stand up provide structural strength If depleted, plants __________________ Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells