* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurological Injuries - toggenburg ski patrol
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
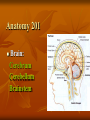
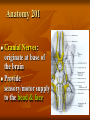
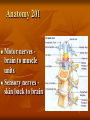
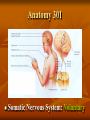
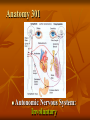
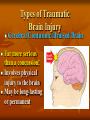
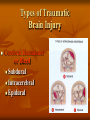
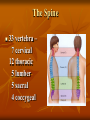
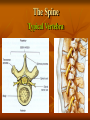
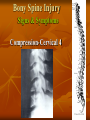
Neurological Injury Management Objectives Review the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system and spinal column Identify the types and mechanisms of head and spine injuries, and describe their features Describe the assessment of head and spine injuries Neurological Injuries Responsible for one half of the deaths that occur secondary to trauma The major cause of long-term disability Caused most frequently by falls and MVA’s Can be prevented in part by helmets Anatomy 101 Neuron: nerve cell Peripheral neurons (nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord) are sheathed with a protective fatty coating called myelin Nerve impulses are transmitted across synapses (junctions) Anatomy 101 Central Nervous System: Brain Spinal Cord Anatomy 101 Peripheral Nervous System: spinal nerves and their branches Anatomy 201 Meninges: protective triple layer cover Dura mater = outer layer Arachnoid = middle layer Pia mater = inner layer Cerebral spinal fluid circulates within the Arachnoid Anatomy 201 Brain: Cerebrum Cerebellum Brainstem Anatomy 201 Cranial Nerves: originate at base of the brain Provide sensory/motor supply to the head & face Anatomy 201 Motor nerves brain to muscle units Sensory nerves skin back to brain Anatomy 301 Somatic Nervous System: Voluntary Anatomy 301 Autonomic Nervous System: Involuntary Traumatic Brain Injury Severity depends on the amount of primary and secondary brain injury Primary Injury: THE INITIAL TRAUMA Main cause of secondary injury: HYPOXIA Traumatic Brain Injuries Categories: Open or Closed Open Closed Traumatic Brain Injuries Forces: Shearing and Compressive Shearing Compressive Types of Traumatic Brain Injury Concussion: Temporary loss or alteration of part or all of the brain’s abilities to function, without apparent physical damage to the brain Types of Traumatic Brain Injury Cerebral Contusion: Bruised Brain Far more serious than a concussion! Involves physical injury to the brain May be long-lasting or permanent Types of Traumatic Brain Injury Cerebral Hematoma or Bleed Subdural Intracerebral Epidural Traumatic Brain Injury General Signs & Symptoms Headache Dizziness Nausea/vomiting Amnesia Traumatic Brain Injury General Signs & Symptoms Decreasing level of responsiveness Confusion Combativeness Loss of responsiveness Assessing Traumatic Brain Injuries Level of Responsiveness (LOR) LOR usually corresponds to the extent of loss of brain function Progressive deterioration usually indicates serious brain injury Assessing Traumatic Brain Injuries Level of Responsiveness (LOR) AVPU SCALE A = Alert V = Verbal P = Pain U = Unresponsive Obtain Baseline Monitor Frequently (q. 5-15 minutes) The Progressive Downward Spiral Brain Swelling Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Hypoxia Further Secondary Injury More Swelling Increased ICP Signs Of Increasing Intracranial Pressure The General Signs of Head Injury Described Previously PLUS Change in pupil size and reactivity to light Slowing pulse Rising BP. Signs Of Increasing Intracranial Pressure The General Signs of Head Injury Described Previously PLUS Change in respiration Unilateral weakness Incontinence Seizures Urgent Interventions Presume C-Spine injury: immobilize neck Open airway, administer oxygen Do not hyperventilate Treat bleeding and shock Urgent Interventions Prevent aspiration of vomit/secretions Transport immediately Elevate head 6”, Transport head uphill The Spine 33 vertebra – 7 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumber 5 sacral 4 coccygeal The Spine Typical Vertebra Bony Spine Injury Signs & Symptoms Usually produced by compression or bending trauma Pain at injury site Localized acute tenderness Self-splinting or guarding Deformity – usually not obvious Bony Spine Injury Signs & Symptoms Compression-Cervical 4 Bony Spine Injury Signs & Symptoms Bending (Flexion) Trauma Cervical 5 on Cervical 6 Vertebra Spinal Cord Injury Significance of spine injury depends whether spinal cord injured Spinal Cord damage more common with neck injury than mid/lower back injury Spinal Cord Injury Mechanism: axial compression, hyperextension, hyperflexion, rotation The higher the cord injury, the more nerve fibers damaged Cervical 5 Thoracic 5 Types of Spinal Cord Injuries Paraplegia - paralysis of both legs Quadriplegia - paralysis of both arms and both legs Hemiplegia - paralysis of an arm and leg on the same side Spinal Cord Injury Signs and Symptoms Abnormal sensation Loss of sensation Muscle weakness or paralysis Spinal Cord Injury Signs and Symptoms Signs of neurogenic shock Difficulty breathing Incontinence Priapism Emergency Care - Spine Urgent interventions for obstructed airway, abnormal breathing, bleeding Stabilize head and neck manually Care for other injuries Emergency Care - Spine Transfer to spine board with proper technique to minimize movement Immobilize on long spine board with CID; apply cervical collar