* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Study Guide
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
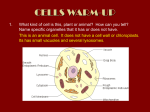
Name: Date: Period: Cells Study Guide 1. Relate “cell” to “organelles.” 2. List two things that organelles do for cells. 3. Explain how scientists know that cells are alive. 4. According to cell theory, explain how animals, plants, fungi, protists, and bacteria are similar. 5. According to cell theory, explain where new cells come from. 6. Complete the graphic organizer below. Prokaryotes Require energy? (Yes/No) Divide? (Yes/No) Make protein? (Yes/No) Have DNA? (Yes/No) Have cell membrane? (Yes/No) DNA contained in nucleus? (Yes/No) Have membrane-bound organelles? (Yes/No) Multicellular or unicellular? SKIP Small or large? 8. List three characteristics that prokaryotes and eukaryotes share. 9. List three differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 10. Explain why the organelles of a eukaryote must be “membrane-bound.” 11. List four examples of eukaryotic cells. 12. Give an example of a prokaryote. Eukaryotes 13. Explain how protists are different from other eukaryotes. 14. Explain what is meant by the following statement: “most eukaryotic cells are highly specialized.” 15. Identify a cell’s most important job. 16. Explain how organelles in a eukaryotic cell are separated from the rest of the cell. 17. Identify the function of the cell membrane. 18. Explain why cell membranes are made from lipids. 19. Differentiate between a cell membrane and a cell wall in terms of what they do and what they are made from. 20. Identify the main function of the nucleus. 21. Explain why the nuclear envelope is dotted with pores. 22. Identify the main function of ribosomes. 23. Identify the main function of rough ER. 24. Identify the main function of smooth ER. 25. Identify the main function of the Golgi apparatus. 26. Identify the main function of the vacuole. 27. Identify the function of the central vacuole in plants. 28. Identify the function of the contractile vacuole in unicellular protists. 29. Identify the function of lysosomes. 30. Explain how lysosomes are able to break down large polymers such as starch or cellulose. 31. Identify the main function of mitochondria. 32. Explain why all cells (including plant cells) need mitochondria. 33. A molecule of starch enters the bloodstream from the stomach and makes its way to a leg muscle cell. After it enters the cell, describe how the cell’s lysosome and mitochondria will process the starch for energy. 34. Identify the main function of chloroplasts. 35. List two types of eukayotes that contain chloroplasts. Types of Cells Graphic Organizer Animal Type of cell Size Complexity Specialization Multicellular/ unicellular Contains DNA? Location of DNA Cell membrane Cell wall Ribosomes (not membranebound) Rough ER Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Central vacuole Contractile vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplasts Cytoskeleton Plant Fungus Protist Bacteria