* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
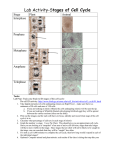
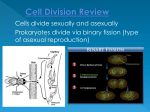
Asexual Reproduction Mitosis DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? 1 1 DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? Asexual Reproduction Mitosis DSQ: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei. How does mitosis differ in plants and animals? ANALYZE (break apart, study the pieces) There is a question within a question in this DSQ Can you identify the question within the DSQ? 8 8 Vocabulary Needed Chromosomes- structures in the nucleus that contain DNA DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid, is the master copy of an organism’s information code. Chromatin- hereditary material in a cell’s nucleus, it coils into the form of chromosomes when a cell divides Centromere-where the double stranded chromosome is held together How do little elephants grow up to be BIG elephants? The process of asexual reproduction begins after a sperm fertilizes an egg. Skin cancer - the abnormal growth of skin cells - most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. Cell that reproduce by asexual reproduction reproduce constantly. Animated Mitosis Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase & Cytokinesis Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase • Nucleus CELL MEMBRANE Cytoplasm Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • • • Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. (Only in animal cells). Chromosomes become fully visible. The nuclear membrane disappear Spindle fibers form between the poles.(Only in plants). Centrioles Sister chromatids Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Spindle fibers Centrioles Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers and line up across the center of the cell. Centrioles Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • • • Two new nuclei form. Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods) and become harder to see. Centrioles and spindle fibers start to disappear. A nuclear membrane starts to form around each group of chromosomes. Mitosis ends. Nuclei Chromatin Nuclei Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes. Animal Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase Plant Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 29 - Cell Division 30 30 http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm