* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Outline
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
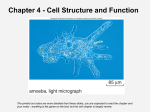
Chapter Outline 5.1 The History of Eukaryotes A. Endosybiosis of prokaryotes to the first eukaryotes B. Evolution of organelles and membranes 5.2 Form and Function of the Eukaryotic Cell: External Structures A. Locomotor Appendages: Cilia and Flagella 1. Structurally different from prokaryotes 2. Function-motility B. The Glycocalyx-extracellular matrix 1. Polysaccharide 2. Functions Include: a. Adherence b. Communication via receptors and cytokines C. Boundary Structures-cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane 1. The Cell Wall 2. The Cytoplasmic Membrane a. Structure- Phospholipids & sterols b. Selectively permeable barrier 5.3 Form and Function of the Eukaryotic Cell: Internal Structures A. The Nucleus: The Control Center 1. Structure-nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nuclear pores 2. Contents-Chromosomes, histone protein B. Endoplasmic Reticulum: 1. Rough ER- ribosomes –protein synthesis 2. Smooth ER-lacks ribosomes- lipid synthesis and detoxification C. Golgi Apparatus: 1. Processing and sorting center for newly synthesized proteins 2. Protein modification-lipids added, carbohydrates added D. Lysosomes- low pH, digestive enzymes E. Vacuoles- plant cells only, storage of water, wastes, poisons F. Mitochondria: Energy Generators of the Cell 1. Structure- outer membrane, inner membrane (cristae) and matrix 2. DNA, ribosomes 3. Aerobic respiration G. Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis 1. Structure- triple membrane, thylakoid membrane, stacks of grana 2. Photosynthesis-light and carbon dioxide to form ATP and sugar H. Ribosomes: Protein Synthesizers 1. Eukaryotic 80S, a large (60S) and a small (40S) subunit 2. Translation of codons into amino acids I. The Cytoskeleton: A Support Network 1. Cytoplasmic Matrix 2. Cytoskeleton a. Microfilaments b. Microtubules 5.4 Eukaryotic-Prokaryotic Comparisons and Taxonomy of Eukaryotes Microorganisms A. Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells vary in structure, size, metabolism, motility and shape B. Taxonomic groupings of Eukaryotes are based on 1. Level of organization 2. Body plan 3. Cell structure 4. Nutrition and metabolism 5. Genetic characteristics 5.5 The Kingdom of the Fungi A. Morphology 1. Hyphae 2. Yeasts 3. Pseudohypha 4. Dimorphic B. Fungal Nutrition 1. Heterotrophic 2. Saprobes C. Reproductive Strategies and Spore Formation 1. Asexual Spore Formation a. Sporangiospores b. Sporangium c. Conidia i. Arthrospore ii. Chlamydospore iii. Blastospore iv. Phialospore v. Microconidium and Macroconidium vi. Porospore 2. Sexual Spore Formation a. Zygospores b. Ascospores c. Basidiospores D. Major Groups of Fungal Classification 1. Phylum I – Zygomycota (Also Zygomycetes) 2. Phylum II – Ascomycota (Also Ascomycetes) 3. Phylum III – Basidiomycota (Also Basidiomycetes) 4. Phylum IV – Chytridomycota 5. Fungi That Produce Only Asexual Spores (Imperfect) E. Fungal Identification and Cultivation F. The Roles of Fungi in Nature and Industry 5.6 Survey of Protists: Algae A. Photosynthetic Protists 1. Morphology B. Nutrition and habitat C. Importance 1. Oxygen producers 2. Nitrogen fixation 3. Neurotoxins 5.7 Survey of Protists: Protozoa A. Protozoan Morphology 1. Motile 2. Many free living, some parasitic B. Nutritional and Habitat Range C. Life Cycles and Reproduction 1. Trophozoite 2. Cysts 3. Conjugation D. Protozoan Major groups 1. The Mastigophora (Also Called Zoomastigophora) 2. The Sarcodina (Amoebas) 3. The Ciliophora (Ciliates) 4. The Apicomplexa (Sporozoa) E. Importance 1. Food web 2. Medical and economic due to pathogenic forms 5.8 The Parasitic Helminths A. Major groups 1. Nematodes 2. Cestodes 3. Trematodes B. General Worm Morphology C. Life Cycles and Reproduction 1. Sexes separate or Hermaphroditic 2. Intermediate or Definitive Host D. Distribution and Importance of Parasitic Worms