* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 7.1 Guided Notes
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
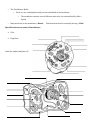
Name ______________________________ Class Period _______________ CP Biology - Cell Structure and Theory: Guided Notes Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke - 1665 Anton Van Leeuwenhoek – 1674 Robert Brown – 1832 Matthias Schleiden - 1838 Theodor Schwann - 1839 Rudolf Virchow - 1855 Ernst Ruska – 1939 Three Types of Microscopes Compound Light Microscope Utilizes WHAT to view specimen? What does it allow you to see? Total Magnification “Pro” “Con” Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) 7.2 - Cell Structure The Discovery of the Cell – THE CELL THEORY 1. 2. 3. Prokaryote Prokaryotes • Prokaryotic cells are generally _______________________________ and ______________________________ than eukaryotic cells. • • The organisms we call bacteria are prokaryotes. Eukaryotes • Eukaryotic cells are generally __________________________________ and ____________________________. • Most contain dozens of____________________________________ and _________________________________ • • Eukaryote Many eukaryotes are highly specialized. • Types of eukaryotes: plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Cell Structure • Cell Diversity – Are specialized to perform specific functions • • • • • • Compare Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cells • • • • • • • • • • Animal Cells • Cell Organization – Eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: • Cell Organization – ________________________________________________ specialized structure that performs important functions within a cell. • Literally “little organs.” • Cell Structures Organelle Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Cytoplasm Vacuoles Vesicles Function/ Information Lysosomes Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough & Smooth Golgi Apparatus Mitochondria Chloroplasts *Plant Cell* Cytoskeleton Microtubules Microfilaments Cell Wall *Plant Cell* • Cell Membrane – Is the cell _______________________________________________ !! – Regulates what _________________________________ and _____________________________________ the cell. – The cell membrane is ____________________________________ ____________________________________ • Some substances can pass across them and others cannot. – Cell membranes are made of double-layer of _____________________________________. • Called the ______________________________ ____________________________________. – Is strong and flexible barrier between the cell and its surroundings • The Fluid Mosaic Model – There are also carbohydrates and proteins embedded in the membrane. • • The membrane contains several different molecules, but remains flexible (Like a liquid) Many molecules in the membrane = Mosaic Special Structures on some cell membranes Cilia - Flagellum – Label the animal and plant cell: Flexible and molecules constantly moving = Fluid