* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Cell Transport Notes Packet - Dallastown Area School District
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
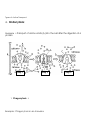
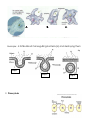
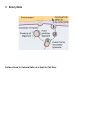
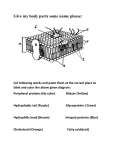
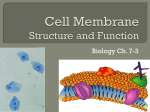
Unit 4 = Cell Transport Honors Biology Cell Membrane Structure and Processes that Transport Molecules across the Membrane which aid in maintaining homeostasis A. The Structure of the Cell Membrane 1. Refer to as the Fluid Mosaic Model 2. Diagram of the Cell Membrane Structure: C D Letter A. The Phospholipid Bilayer B A Letter B. A Transport Protein (also called Channel or Carrier Proteins) Letter C. Receptor Proteins Letter D = Recognition Proteins (glycoproteins with carbohydrate branches) Cholesterol = B. Processes that Transport Materials across the Cell Membrane (to allow materials either into or out of a cell) *Two categories of Processes = _______________ process VS ________________ Processes* 1. _____________________ Transport Examples of Processes that are forms of Passive Transport: a. _____________________ Examples in Everyday Life = Example in a Cell = A Human Muscle Cell Respiring Aerobically: b. _________________ = Example #1 = A Red Blood Cell in an _________________ Solution Outside of the cell = Example #2 = A Red Blood Cell in a _________________ Solution Outside of the cell = Example #3 = A Red Blood Cell in a _________________ Solution Outside of the cell = c. _________________ _____________ = Molecules of _____________ Exterior of the Cell High Phospholipid Bilayer Cytoplasm of the Cell Low Step #1 2. Active Transport = Step #2 Step #3 Types of Active Transport: a. Endocytosis: Example = Transport of Amino Acids (A) into the cell after the digestion of a protein Step 1 Step 2 1. Phagocytosis = Example: Phagocytosis in an Amoeba Step 3 A. B. C. Example: A White Blood Cell engulfing bacteria (H) and destroying them Step 1 Step 2 2. Pinocytosis Step 3 B. Exocytosis Surface Area to Volume Ratio as a Limit to Cell Size: