* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell - Wando High School
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
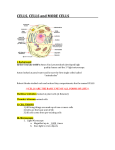
Chapter 7 – The Cell Name ___________________________________ Discovery of the Cell • Robert Hooke (______) – English scientist – looked at a _______________ (oak cork) through a ________________________ (____ lenses). – observed _________________________ structures – called these structures _______ because they reminded him of ______________ – only saw the outer walls (___________) because ________________________ • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (________) – Dutch fabric merchant and __________ _____________ – looked at ________________________ _________ through a ______________ (___ lens and natural light). – observed living cells; called some “________________” – some of the small “animalcules” are now called ____________ Development of Microscopes • van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was considered a simple light microscope because it used _____ ____________________________ • • Hooke’s microscope was compound because it used ________________ In the 200 years after Hooke, compound light microscopes have improved to magnify objects ____ times using ________ and a ___________ • Electron microscopes use a beam of electrons to magnify objects ____________! – This power allows us to see the structures _______ _______ and _____________________ Electron Microscopes • Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) – ____________________________________________________________ 1 • Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) – ___________________________________________________________ • Scanning Tunneling Microscope – _________________________________________________________________ Compound Microscope 2 Cell Theory • Two scientists, Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann (________) expanded upon Hooke’s observation of “______” • Their observations in plants and animal cells have been summarized as the ______________ The Cell Theory • 1. ________________________________________ • 2. ________________________________________ __________________________________________ – __________ organisms – made of __ cell that must perform _____ life’s activities – _________ organisms – made of _____________ cell. Each cell performs _______ of the major functions of life • 3. ________________________________________ – Before the cell theory, people did not know where these cells came from. People learned that a cell ________ to form ___ ________________________ – The ability of a cell to divide is the basis for • all ____________________ (sexual and asexual) • ____________________ of all multicellular organisms Types of Cells • There are two broad groups of cells – Prokaryotes • ________ have membrane-bound organelles – Eukaryotes • • ______ have membrane-bound organelles Organelle – Structure within a cell that is surrounded by a _________ and has a specific ___________ for cell survival 3 Eukaryotes • ___________ a membrane bound nucleus – DNA is _______ within the nucleus • _____ Contain membrane-bound organelles • Eukaryotes may be ____________ (algae and yeast) or _____________ (plants and animals) Plasma Membrane (or Cell Membrane) • • __________ of the cell Controls what goes in and out of the cell through the __________________________ – Keeps some things ____ and lets some things ___ • Maintains cell’s ___________________ Cell Wall • Found _________ the cell membrane Cell Wall • Gives the cell added __________________________ • Made of the carbohydrate, ______________ • This mesh of cellulose is porous and allows _________ to pass through • _____________________________________________________ have cell walls • Animals ______________ Cytoplasm • • • ___________ is a semi-fluid material inside the cell It contains the _____________ and __________ in the cell It is bound by the __________________ 4 * Nucleus and Nuclear Envelope • Functions in the _____________ of the cell • Contains the ___________ which are composed of ____________ • The nuclear envelope is a membrane that * * Important parts to know – ______________ the nucleus – Regulates the materials that pass between the ____________ and the _____________ • In eukaryotic cells (___________ ____________) Mitochondria • This is the site of _______________________, a process that provides the cell with _____________ • The “___________________” • The ______ energy a cell needs, the ________ mitochondria they may have – For example, a _______ cell would need more mitochondria than a ______ cell because it requires more ____________ to do its job • In ____________ cells Chloroplast • • Contains the green pigment __________________ __________ absorbs energy from ________ to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar during ____________________ • Only found in __________ ________________ 5 Ribosomes • • Ribosomes are the site of __________________ Can be found – floating _______ in the cytoplasm – or on the ____________________________________ • In ____________________________________ Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • ER is a complex, extensive network that ____________ materials throughout the _____________ of the cell • _________ ER: – _______ ribosomes attached • _________ ER: – __________ ribosomes • In ____________ only Golgi Apparatus • Function: ________, _______, ________, and ________ molecules _____ the cell or _________ the cell • In _____________ Lysosomes • Small organelles containing _________ ___________ to break down ____________, _________________, _______, and ______ into particles that can be used by the rest of the cell • In ______________ 6 Vacuoles • Sac-like structures that ______________ such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates • Plants have __________ vacuole that also helps _____ _____________ to flowers and leaves • Animal cell vacuoles are much _______ than plant cell vacuoles • In __________ Cilia and Flagella • Function: Helps to move _______ or ________ ______________; some organisms use them to _____________. • Cilia – _____, _________, _______ projections that move in a _________ motion – _________________________ • Flagella – __________ projections that move in a _______ motion – _____________________________ Prokaryotes • ___________________________ – DNA is __________ in a nucleus or arranged in ___________________ • * ________ have most membrane-bound organelles – They ___ have _______________ for protein synthesis – They _______ have ____________. They get their energy from the ____ or from _________________ in * * *Cytoplasm the environment • Many prokaryotes are _________ • This cell type includes all _______ 7 Prokaryotes vs. Plants vs. Animals Eukaryotes Organelle Prokaryotes Plants Animals Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Nucleus DNA Mitochondria Chloroplasts Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Cytoplasm Cilia or Flagella 8