* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Notes - Thunderbird High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
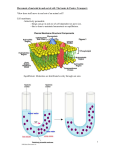
Cell Transport Notes Homeostasis All living things, from cells to large organisms, maintain very stable internal conditions _________________ Water content _________ _____________ Salt levels ________________: __________ level of internal ________________ Homeostasis and Cell Transport Cell membranes help organisms ________________ homeostasis by ______________ what _________________ may enter or leave cells Water and other substances are moved in and out of a cell in two ways: 1. _________________ transport 2. _________________ transport Passive Transport Passive transport: when substances can cross the membrane _________________ _________________from the cell Types of Passive transport 1. ____________________ 2. ________________ ________________ 3. _____________ Diffusion Diffusion: _____________________ ________ _________________ (______ WATER) from an area of _________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration Requires _____ ___________ High Low Concentration Gradient Concentration Gradient: The ________________ in concentration of molecules across a space When molecules go from _______ concentration to _____ concentration, they are said to be moving __________ the concentration gradient Equilibrium Equilibrium: Eventually the _____________________ of molecules will be the __________ (equally spread out) this balance in concentration is called Equilibrium Diffusion Across Membranes The _______________ of a molecule ___ ___________ across a cell membrane depends on the _____, type, and chemical nature of the molecule Molecules that are small such as _______ and ______ will pass through the membrane by diffusion Very _____ _____________ like _____________ or ions (charged particles) may _______ be able to get through by ________________ Facilitated Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion: ___________ across a membrane with help of ______________ proteins Used for molecules that are not soluble in lipids or are too large to pass through the pores in the membrane Substances move down the concentration gradient (______ ____ _____) _____ __________ Osmosis Osmosis: diffusion of _______________ across a membrane from areas of _______water concentration to areas of _______ water concentration _____ __________ High Low Molecular Movement in Cells ______________ solution: ___________ concentration of __________ _________cell WATER _________ ________ cell Water will go from ______ to ______ concentration until equilibrium is established Hypertonic solution: ___________ concentration of _________ _______ cell WATER ________ ______ OF cell Water will go from _______ to ______ concentration until equilibrium is established Isotonic solution: _________ ____________of WATER inside and outside cell WATER ______________ _____________ Active Transport Active Transport: movement of molecules from an area of _____ concentration to an area of ______ concentration _________ __________!!! ________ Low High Concentration Gradient Concentration Gradient: The difference in concentration of molecules across a space When molecules go from _______ concentration to _______ concentration, they are said to be moving _____ __________________________ Active Transport Cell Membrane Pumps Proteins in the cell membrane that move (pump) substances up the concentration gradient ______ __________ _____ to work Active Transport of Macromolecules Some molecules (such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, etc….) are too large to cross the cell membrane by passive transport or by active transport through cell membrane pumps. These macromolecules move across the membrane in two ways 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ Endocytosis When a cell engulfs a substance and _________ ____ _____ A type of active transport because it ___________ _____ Types of Endocytosis _________________ transport of fluid into the cell (______________) _________________ engulfment of large particles or cells into the cell (______________) _________________ When a cell _______ ________ a particle Getting rid of solid wastes Vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the cell membrane, releasing their contents out of the cell