* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
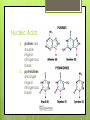
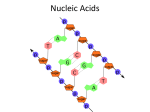
Nucleic Acids Hereditary Material Nucleic Acids VI. nucleic acids transmit hereditary information by determining what proteins a cell makes A. two classes of nucleic acids found in cells: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) 1. 2. DNA carries the genetic information cells use to make proteins RNA functions in protein synthesis according to mechanisms Nucleic Acids B. nucleic acids are polymers made of nucleotide monomers 1. a nucleotide consists of • • • a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) one or more phosphate groups, and a nitrogenous base, an organic ring compound that contains nitrogen Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids 2. 3. purines are doubleringed nitrogenous bases pyrimidines are singleringed nitrogenous bases DNA vs. RNA C. D. DNA typically contains the purines adenine (A) and guanine (G), and the pyrimidines cytosine (C) and thymine (T) RNA typically contains the purines adenine (A) and guanine (G), and the pyrimidines cytosine (C) and uracil (U) Nucleotides E. nucleotides are fastened together by phosphodiester bonds 1. 2. 3. F. the phosphate group of one nucleotide is fastened to the sugar of the adjacent nucleotide the joining is yet another condensation reaction the way that the are joined creates a polynucleotide strand with 5’ and 3’ ends the sequence of the 4 bases fastened to the sugar-phosphate backbone is genetic information Phosphodiester Bond DNA G. DNA is typically a double stranded molecule the two strands twist into a double helix hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of opposite strands hold the strands together the two strands are antiparallel RNA H. RNA is typically a single stranded nucleic acid molecule, having only a single polynucleotide chain Related Compounds I. J. “related compounds” – nucleotides, modified nucleotides, dinucleotides some single and double nucleotides with important biological functions: 1. 2. 3. adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an important energy carrying compound in metabolism cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a hormone intermediary compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an electron carrier which is oxidized or reduced in many metabolic reactions