* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.13 notes
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
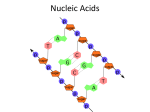
4.13 Nucleic Acids Contain the Blueprint for Life Nucleic Acid • vital to cell function (used for protein synthesis) • the building block of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids together during the synthesis of protein DNA • nucleotides form a double helix which makes up a chromosome (structure that carries genetic information) and is found in a cell’s nucleus (see figure below) • stores the information needed for protein synthesis • by controlling enzyme production, DNA controls all the activities (chemical reactions) of a cell Chromosome DNA nucleotide in box sugar and phosphate nitrogen base