* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
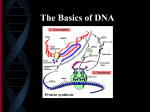
Unit 6 Study Guide DNA Replication 1. Proteins determine what? 2. What is the monomer of proteins? 3. Who initially discovered the helix shape of DNA and was she (at the time) recognized for the accomplishment? 4. What did Watson and Crick do to get the Nobel Prize? 5. What are the 3 parts of the nucleotide (include amounts of each). 6. Approximately how many base pairs are on one chromosome? 7. When grouping the nitrogen bases by similar characteristics, the purines have ___________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of ______________ and _______________. 8. When grouping the nitrogen bases by similar characteristics, the pyrimidines have ________________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of _______________ and ___________________. 9. Singular ringed bases pair with double-ringed bases when forming DNA, what are the 2 combination of base pairs? 10. What is the bond between the sugars and the phosphates and the nitrogen bases to the sugars? Is it a strong bond? 11. What is the bond that links the complementary nitrogen bases together? Is it strong? 12. What are the 4 steps of DNA replication? RNA Transcription 13. What does RNA stand for? 14. What is the function of RNA? 15. What are the 4 major differences between DNA and RNA? Unit 6 Study Guide 16. What brings a copy of information from the DNA to the ribosome? 17. What binds to the mRNA on 1 end and brings an amino acid on the other? 18. What makes up part of the ribosome and hold the mRNA during translation? 19. Which RNA makes the proteins? 20.What is the process that makes mRNA from DNA and where does it occur? 21. What are the 4 steps of transcription? 22. What are the segments of mRNA that are not needed and left in the nucleus like “garbage”? 23. What is the segment of RNA that leaves the nucleus to be read and “expressed”? Translation and Protein Synthesis 24. What process makes proteins at the ribosome by using the DNA code? 25. What are the 4 steps of translation? 26. What is the 3 nucleotide code on the mRNA called? 27. What is the 3 nucleotide matching code on the tRNA called? 28. What is on the opposite end of the Anticodon? Unit 6 Study Guide 29. What are a chain of amino acids called? 30. 1 codon codes for how many amino acids? 31. Is the order of the amino acids important? Why? 32. Can you change the order, add, or take an amino acid out and NOT change the protein? 33. What is the mRNA start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 34. What are the 3 mRNA stop codons and what amino acids do they code for? 35. What process makes DNA? 36. What 3 processes in order make protein and list the location of each process? 37. What is the definition of a mutation? 38. What are the 3 possible results of a mutation? 39. What type of mutation does NOT change the amount of bases because it just substitutes a base for another base? 40.What type of mutation changes the number of bases because it adds or deletes a base? 41. Which mutation does NOT always affect the protein/gene? 42. Which mutation ALWAYS changes the protein/gene?