* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name:
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
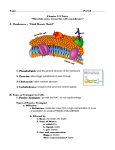
Name: Date: Period: In & Out of the Cell: Web Quest (Cell Transport) Part 1 – Cell Membrane GO TO THIS WEBSITE: http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/me mbrane_transport/membrane_transport.htm 1. Read the “Overview” of a cell membrane. Click on “Continue” to observe the animation. Draw a cell membrane and label all the parts as you step through the animation. 2. Click “Continue” again to observe “Osmosis and Diffusion”. Why does the balloon on the left get larger? 3. Click “Continue” to observe “Passive Transport”. NOTE: Osmosis and diffusion are forms of passive transport. This animation describes a special case of passive transport called facilitated diffusion. Larger molecules such as glucose can then enter the cell by means of a special pathway. List the 3 steps of how molecules like glucose get into the cell. 4. Click on “Continue” to observe “Active Transport”: a. In what kind of cells is this “sodium-potassium pump” commonly found? __________ b. What form of chemical energy is required for active transport to take place? __________ b. What ion is moved into the cell? _____________ How many? __________ c. What ion is moved out of the cell? ______________ How many? __________ Part 2 – Construction of a Cell Membrane http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=ap1101 Click through to page 4: 1. Name the 3 globular-shaped proteins that make up part of the cell membrane. ________________ ________________ ________________ 2. Most of the cell membrane is made up of phospo ____________. 3. The “tails” are __________________ and therefore face inward and away from water. 4. The “heads” are ________________ and face toward the water. 5. The “heads” and “tails” are arranged in a _______________ bilayer. 6. The fibrous proteins serve as _____________________________________ 7. One type of _________________________ allows water to pass through. 8. Integral (channel) proteins transport ________________ for the cell. 9. ___________________ is found only in animal cells. It stabilizes the cell membrane as well as making less permeable to water soluble substances. Now, construct a Cell Membrane by answering questions one through ten in the computer based activity. Part 3 Solutions http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_solution.html 1. What is a solution? 2. Explain the difference between the solute and solvent. Part 4 Osmosis http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/science/sbi3a1/Cells/Osmosis.htm 1. What is osmosis? ______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. A hypertonic solution has a _______concentration of _________ relative to another solution (like the cytoplasm of the cell). 3. What happens to a cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution? (Run the animation) • Which way does the water move? _____________________________ • What happens to the cell? __________________________________ 4. A hypotonic solution has a _________________concentration of __________ relative to another solution (like the cytoplasm of the cell). 5. What happens to a cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution? (Run the animation) • Which way does the water move? ___________________________ • What happens to the cell? _________________________________ 6. An isotonic solution has the _____________ concentration of ____________ as another solution (like the cytoplasm of the cell). • Which way does the water move? ______________________________ • What happens to the cell? ___________________________________ * The fluid that surrounds the ___________________ is isotonic. Part 5 Diffusion and Osmosis http://www.mun.ca/biology/Osmosis_Diffusion/tutor2.html 1. Read the overview and define all the terms by clicking on them: • Diffusion – • Passive Transport – • Concentration Gradients – Now, click the back button… Scroll down to example #1 (how perfume spreads throughout a room) and read it. Next scroll down to example #2 (salt dissolving in water) and read it. Next scroll down to example #3 (diffusion will occur through a permeable membrane) AND ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: 2. What is the solute concentration in side A? ________________ What is the solvent concentration in side A? _________________ 3. What is the solute concentration in side B? ________________ What is the solvent concentration in side B? _________________ 4. Fill in the diagram below of the two sides (A and B) and show the movement of solute and solvent across the permeable membrane. Label the concentrations of solute and solvent under both sides. Then answer the related questions: Solute A Solvent B Solute diffuses from side ____ to side ____ A B Solvent diffuses from side ____ to side ____