* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midterm Review - juan
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
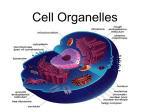
Midterm Review Name_________________ DNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Label the numbered parts in the diagram of DNA 1 = __________________________________________ 2 = __________________________________________ 3 = __________________________________________ 4 = __________________________________________ Circle a nucleotide on the DNA to the right. 2. Provide at least 2 reasons why DNA is so important to living organisms. 3. Use the following DNA complete the steps below: TTT TGG CAA GGG AAA Replicate it:______________________________________DNA Transcribe it: ____________________________________mRNA Translate it: _____________________________________Amino Acid Sequence Circle one codon you wrote in the above spaces. Place a box around one anticodon you wrote in the above spaces. 4. What is the job of mRNA in transcription? 5. What is the job of tRNA in translation? Label the picture below: This box is a process name. Cell Structure and Function 1. Draw and label a plant cell and animal cell. Include the following organelles and structures in the appropriate cells: vacuole, nucleus, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast, mitochondria. 2. Describe the differences and similarities between plant and animal cells. 3. Make a venn diagram outlining the similarities and differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Use the following terms: ribosomes, nucleus, membrane bound organelles, plasma membrane, circular DNA, linear DNA, bacteria, plants, animals, fungi, protists 4. Complete the chart for the 4 main classes of organic molecules. Organic compound Monomer What it’s used for in living organisms (purpose and (building block) importance) Give an example in a living thing. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids 1. What structure distinguishes a eukaryote from a prokaryote? ________________________________ 2. What shape is a plant cell? ____________________ An animal cell? __________________________ 3. What part of the cell is describe as selectively permeable? ____________________________________ 4. If you place a few drops of food coloring in a glass full of water, eventually all the water is colored. This is due to the process of _______________________________________ 5. For each of the structures listed, indicate whether it is found in PLANTS (P), ANIMALS (A), or BOTH (B) _____ Chloroplasts ______ Cell Membrane ______ Nucleus ______ Cell Wall ______ Mitochondria 6. Which cell part is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis within the cell? _____________________________________________________________ 7. Know the function of each of the cell organelles listed: a. Endoplasmic Reticulum ________________________________________________________ b. Cell Membrane ________________________________________________________ c. Ribosome ________________________________________________________ d. Mitochondria ________________________________________________________ e. Nucleus ________________________________________________________ Label the cell below. Enzymes: 1. Draw an enzyme with its active site labeled, a substrate, and products. 2. What group of organic molecules are enzymes? What are enzymes made of? 3. Draw a graph of an enzyme whose optimum temperature is 23 degrees Celsius. Photosynthesis and Respiration 1. Answer the following questions about photosynthesis. a. What organisms undergo photosynthesis? b. Where does it occur in the cell? c. What reactants are required? d. What products are produced? e. Why is it important to us (give at least 2 reasons)? 2. Answer the following questions about cellular respiration. a. What organisms undergo cellular respiration? b. Where does aerobic respiration occur in the cell? c. What is the equation for aerobic cellular respiration? d. What is the purpose of cellular respiration (why can’t we survive without this process?)? e. What are the 2 types of anaerobic respiration? f. Which process, anaerobic or aerobic, releases the most ATP for the cell to use? SCIENTIFIC Method and Microscopes 1. Read the following experiment and answer the questions. a. What is the independent variable in the experiment? _____________________ b. What is the dependent variable? ______________________________ c. Which is the control group? _________ A scientist wants to know if Miracle Grow will increase the number of tomatoes on his tomato plants. To tomato plant A he adds miracle grow; and to tomato plant B he does not add miracle grow. Both plants are given the same amount of light and water. After 6 weeks he counts the number of tomatoes are present on each plant. Plant A = 9 Plant B = 4 3. Microscope Use: a. When first focusing the microscope, which objective do you use? _____________ b. When using the high power objective, which focus knob do you use? ________________ c. What are the three objectives found on the microscopes you used in class? ________________ d. What part of the microscope can be used to adjust the amount of light? _______________________ Cell transport 1. Using your knowledge of osmosis and diffusion, draw and describe (be specific) what happens in the following situations. YOU MUST WRITE the percentage of water inside and outside of the cell. a. You place a red blood cell from your body in a container of distilled water. b. You pour salt water on a patch of grass. c. You place a marine (salt-water) organism in fresh water. 2. In each of the situations pictured, indicate whether the cell will gain water, lose water, or stay the same. In each case, the cell in the beaker is 10% salt. 10% salt 2% salt 30% salt 3. Identify the processes pictured (Diffusion, Osmosis, Endocytosis) 4. Describe active transport across the membrane using the following terms: ATP, low, high, against the gradient Cell Cycle Look at the diagram of the cell cycle. When does the duplication of DNA occur? What is this phase called? What do GI and G2 represent? Does mitosis include cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm)? Put the following stages of mitosis (cell division) in order.