* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
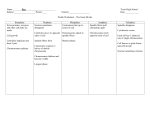
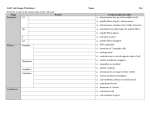
Download Prelab Worksheet Words
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
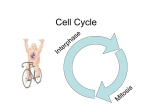
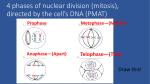
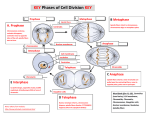
Spindle fibers pull chromatids apart Chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell Cell growth Extra proteins, enzymes and other cell parts are made Nuclear membrane reforms Nuclear membrane disappears Spindle fibers form Centromere connects two halves of double chromosome Chromosomes replicate Each cell has two identical sets of single chromosomes Centrioles duplicate and form two pair Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers Chromosomes thicken and become visible Spindles disappear Centromeres line up in center of cell Centrioles move to opposite sides of cell Cell furrow forms and cells divide Shortest phase Cytokinesis occurs Spindle fibers pull chromatids apart Chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell Cell growth Extra proteins, enzymes and other cell parts are made Nuclear membrane reforms Nuclear membrane disappears Spindle fibers form Centromere connects two halves of double chromosome Chromosomes replicate Each cell has two identical sets of single chromosomes Centrioles duplicate and form two pair Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers Chromosomes thicken and become visible Cytokinesis occurs Chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell Cell growth Extra proteins, enzymes and other cell parts are made Nuclear membrane reforms Nuclear membrane disappears Spindle fibers form Chromosomes replicate Each cell has two identical sets of single chromosomes Centrioles duplicate and form two pair Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers Longest phase Spindles disappear Centromeres line up in center of cell Centrioles move to opposite sides of cell Cell furrow forms and cells divide Shortest phase Spindle fibers pull chromatids apart Centromere connects two halves of double chromosome Longest phase Chromosomes thicken and become visible Longest phase Spindles disappear Centromeres line up in center of cell Centrioles move to opposite sides of cell Cell furrow forms and cells divide Shortest phase Cytokinesis occurs