* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Peptides to Proteins
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
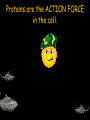
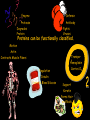
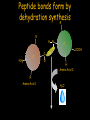
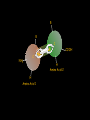
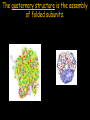
Peptides to Proteins • What are proteins? • Why are proteins important? • How are proteins made? • How do proteins fold? What are PROTEINS? Proteins are large, complex molecules that serve diverse functional and structural roles within cells. Proteins are the ACTION FORCE in the cell. Enzyme Defense Protease Antibody Fights Viruses Degrades Protein Proteins can be functionally classified. Motion Actin Transpor t Hemoglobin Contracts Muscle Fibers Carries O2 Regulation Insulin Controls Blood Glucose Support Keratin Forms Hair and Nails Proteins are chains of amino acids. O C OH N H H Short chains of amino acids are called peptides. Proteins are polypeptide molecules that contain many peptide subunits. N H H Amino acids have an amino group, carboxyl group, R group and hydrogen. R NH2 C H Amino Acid 1 COOH Each amino acid has unique chemical properties. Glycine Histidine Glutamine Glutamate Lysine Cysteine Aspartate Asparagine Arginine Isoleucine Methionine Serine Leucine Proline Alanine Threonine Tryptophan Phenylalanine Valine Tyrosine Peptide bonds form by dehydration synthesis R R NH2 C H Amino Acid 1 H N C O OH H C COOH H Amino Acid 2 H2O R R C COOH NH2 C H Amino Acid 1 H Amino Acid 2 Gene 3’ Nucleus Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) Trp tRNA Ala tRNA Met Met Large Subunit Ribosome Met 5’ Amino Acidtransfer RNA tRNA Ala Empty tRNA Trp Empty tRNA A U G G C C U G G U A G Small Subunit Cytoplasm Ribonucleotides Codon 1 A U G = Methionine Codon 3 U G G = Tryptophan Codon 2 G C C Codon 4 U A G = Stop = Alanine A G C U is the synthesis of proteins in the cell. Primary There are 4 basic Secondary Tertiar y Quaternary L V M H G I Q Y P S E C K T F The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids. N R A P D The secondary structure is primarily composed of alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets. Folding Back and Coiling Alpha Helix Primary Structure Beta-Pleated Sheet The tertiary structure is the protein’s 3D shape. The quaternary structure is the assembly of folded subunits. Proteins must reach their final shape to perform their vital functions Improperly Folded Properly Folded Summary • Proteins are biological workhorses that carry out most of the functions within the cell. • Proteins are large biological molecules that serve diverse functional and structural roles within cells. • Proteins are synthesized during the translation process. Summary cont’d… • Proteins are composed of amino acids that are covalently linked by peptide bonds. • Proteins have four basic levels of structure. However, proteins must fold correctly in order to function properly. THE END!