* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Structures Test Study Guide
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
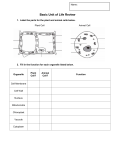
Cellular Structures Test Study Guide HHS biology NAME:____________________________ DATE:__________ BLOCK:____ 1. Which characteristic of prokaryotic organisms makes them different from eukaryotes?______________________________________________________________________ 2. What do typical plant cells have that typical animal cells do not? A. _______________ B. _________ C. ____________________ 3. Because the phospholipid molecules and some proteins are free to move, the plasma membrane is said to be a _________ ________ model. 4. List the following discoveries in the scientific study of living things in chronological order. 1 for the first and 4 for the most recent. ___ Electron microscope ____Light microscope ____Cell theory ____Model of DNA The diagram below represents a single cell eukaryote. On the right is a list of facts concerning the structures found in this cell. Use the diagram and facts 1 through 7 to answer the following question. FACTS 1. Chromatin is present in structure F 2. Respiration occurs in structure G 3. Food molecules increase in structure C if the organism is exposed to light. 4. The organism cannot move. 5. Structure A surrounds the entire cell and is rigid. 6. Structure B is porous 7. Ribosome parts are found in structure E. 5. What type of organism is represented by the diagram? ________________ 6. What is the name of the organelle labeled E? ___________________ 7. What is the name of the organelle labeled D? ___________________ 8. What is the name of the organelle labeled G? ___________________ 9. Usually, the largest organelle in a cell is the _________________. 10. A cell with numerous ribosomes is probably specialized for ________________________________. 11. Orchids were studied to determine if the amount of humidity affected the flowering of these plants. Which of these was the independent variable in this study? _________________________________ 12. These words were written by Robert Hooke in 1665. The pores or cells that Hooke described were really what cell structure? ____________________ 13. Which organelles release chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones?________________ 14. If a cell contains a nucleus, it must be a(n) ____________________ cell. 15. Compared to a skin cell, a muscle cell is likely to have more ___________________. 16. An organism that causes infections in plants and animals, but cannot be seen with a light microscope similar to that used in a high school biology course, is most likely a _________________. 17. The above diagram shows the process of osmosis. Only the water molecules could enter the cell because water molecules are ________________ than the protein molecules. 18. A plant’s green color is due to the presence of which organelle?_____________________ 19. One advantage of electron microscopes over light microscopes is their ________ ______________. 20. List the 3 main ideas of the cell theory. 1. _____________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________ 3. _____________________________________________________ 21. The fluid mosaic model describes a structure with ____________ layers on the outside and _____________ layer on the inside. 22. Which organelle is present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes? ______________________ 23. A microorganism which releases water into its environment to regulate its salinity during osmosis is undergoing a process that is similar to a human being who releases moisture on a hot day. This process that helps keep both the microorganism and the human body fluids in balance is known as________________________. 24. What life form has a prokaryotic cell? ____________________ 25. What is the purpose of the flagellum? ____________________ 26. What might be a result of a disease that causes a thickened plasma membrane? ________________________________________________________________________________ 27. Bacteria are tremendously successful unicellular organisms, yet all large organisms are multicellular. Unicellular organisms cannot grow very large because the ________________ of nutrients into the cell’s interior would be too slow 28. The eukaryotic organism described above should be classified as a ____________. 29. Describe what is happening to the cell in pure water? ________________________________________________________________________________ 30. What organelle functions most like the “brain” of a cell? __________________ 31. The diagram shows a graduated cylinder containing water. From which position will the most accurate measure of the volume of the water be made? Position ____ 32. In the human body, the circulatory system transports and delivers substances. Within the cell, which organelle performs a similar function? _____________________________ 33. The person credited for developing the microscope is _____________________________. 34. In the cell membrane model shown above, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as _________________. 35. Which of these is capable of moving quickly in response to its environment? ____________________ 36. In a plant cell, which cellular structure is responsible for storing food, water, and wastes? __________ 37. The concentration of glucose must be maintained within a fairly narrow range in most vertebrates. This statement is an example of ___________________. 38. Match the scientist with his contibution to the cell theory. A) Theodor Schwann D) Matthias Schleiden B) Robert Brown E) Robert Hooke C) Rudolf Virchow 39. _____ named the cell nucleus 40. _____ stated that all animals have cells 41. _____ stated that all cells come from pre-existing cells 42. _____ stated that all plants have cells 43. _____ named the cell