* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optic Nerves * Jack Baesman
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
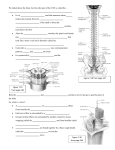
Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal (3 divisions…) Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear (2 divisions) Glossopharyngeal Olfactory Nerves Eric Johnson • • • • • • • • • • • Sensory Nerves associated with sense of smell Contains only axons of sensory, bipolar neurons. Located in upper nasal cavity Olfactory receptor cells carry impulses to neurons in olfactory bulbs Sensory impulses travel from bulbs along olfactory tracts to the cerebral centers where they are interpreted into the sensation of smell. Optic Nerves – Jack Baesman • • • • • • A pair of nerves that leads from the eyes to the brain Enable sight Sensory nerves The cell bodies form ganglion in the eyes, and the axons pass through the optic foramina The impulses are interpreted in the visual cortices of the occipital lobes Bipolar Primarily Motor Arise from the midbrain Pass into the orbits of the eyes The motor fibers transmit impulses to the muscles to: Raise eyelids Move eyes Adjust the amount of light entering the eyes Focus lenses Primarily Motor The motor fibers transmit impulses to move the eyes. Some sensory fibers transmit impulses associated with the condition of the muscles. Smallest cranial nerves Arise from the midbrain Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerves Largest cranial nerves Arise from pons Mixed nerves Sensory portions more extensive than motor portions 3 large branches Ophthalmic Maxillary Mandibular Abducens • • • • 6th cranial nerve Small nerves that originate from the pons near the medulla oblongata Are primarily motor Enter the orbit of the eye and control motor impulses in the muscles that move the eye #7: Facial Nerve By Lauren Sayers • Location: Arises from the lower part of the pons + emerges on the sides of the face. • Function: Sensory fibers transmit impulses associated with taste receptors of the anterior tongue. Motor fibers transmit impulses to muscles of facial expression/tear/salivary glands. Vestibulocochlear nerves (VIII) • Sensory nerves from medulla oblongata • Two parts- vestibular branch and cochlear branch • Vestibular Branch- cell body associated with inner ear and reflexes that help maintain equilibrium. • Cochlear Branch- Cell body houses hearing receptors, these signals pass through medulla oblongata and pons to be sent to the temporal lobe, where they are interpreted and sent back out. Glossopharyngeal nerves 9th pair Arise from medulla oblongata Predominately sensory fibers, carry impulses to linings of pharynx, tonsils, back of tongue Innervate muscles of the pharynx that function in swallowing Vagus Nerves 10th pair Originate in the medulla oblongata , extend down the neck into chest abdomen Somatic and autonomic branches Somatic fibers carry impulses to larynx, help with speech and swallowing Autonomic fibers supply heart and smooth muscles and glands in thorax and abdomen Accessory Nerves 11th pair Originate in medulla oblongata and spinal cord (have cranial and spinal branches) Cranial branch- joins vagus nerve, innervates muscles of soft palate, pharynx, and larynx Spinal branch- drops into neck, innervaes trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles 12th pair Arise from medulla oblongata, into tongue Motor fibers innervate muscles that move the tongue for speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Hypoglossal nerve