* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Passive Transport - ms. tuldanes` science class
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
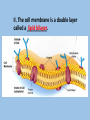
Cell Transport Essential Questions Differentiate passive and active transport. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis. Passive Transport Homeostasis An organism tries to maintain I. ___________: regulating a stable internal environment by ________ enters and leaves what ______ _____ the cell. This is the membrane It is function of the cell _____________. semipermeable or selectively permeable ___________________________________. Food Oxygen Water Cell Wastes CO2 Excess water II. The cell membrane is a double layer lipid bilayer called a __________. Passive Transport III. ______________ A. Cell use ___________. NO ENERGY (Like moving _______) downhill B. Molecules move from an area of ____ High concentration to an area of Low ___ concentration High Low C. Examples Diffusion The movement of molecules 1. ________: _________ high concentration to an area of from an area of _____ low concentration. ___ water though a 2. Osmosis ________: The movement of _____ selectively permeable membrane from an area of ____________________ high concentration to an area of low ____ ___ concentration 3. Facilitated ________________ diffusion uses transport proteins to move other ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane. Substances move through a transport protein called ______________ channel protein that opens and closes to allow substances to diffuse through the membrane A cell is placed in a _________ Hypertonic solution (solution with more solute than the cell Water salt (solutedissolved substance) A cell is placed in a _________ Hypotonic solution (solution with less solute than the cell) Water salt (solute) Water Salt (solute) water Cell shrinks A cell is placed in an _______ Isotonic solution (solution with equal solute concentration with that of the cell) water Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. -DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM water Cell swells and bursts Active Transport Active Transport IV. _______________ energy =___. ATP (Like moving a. A cell uses ______ uphill _____) low b. Molecules move from an area of _____ high concentration to an area of ____ concentration. low equilibrium high ( Do not reach ___________) C. Examples Endocytosis (_____): enter The cell takes in 1. __________ __ material by forming a pouch (________) vacuole around the substance. Exocytosis (___): exit A cell moves a 2. _________ substance to the _______ outside of a cell using a vacuole.